Figure 1.
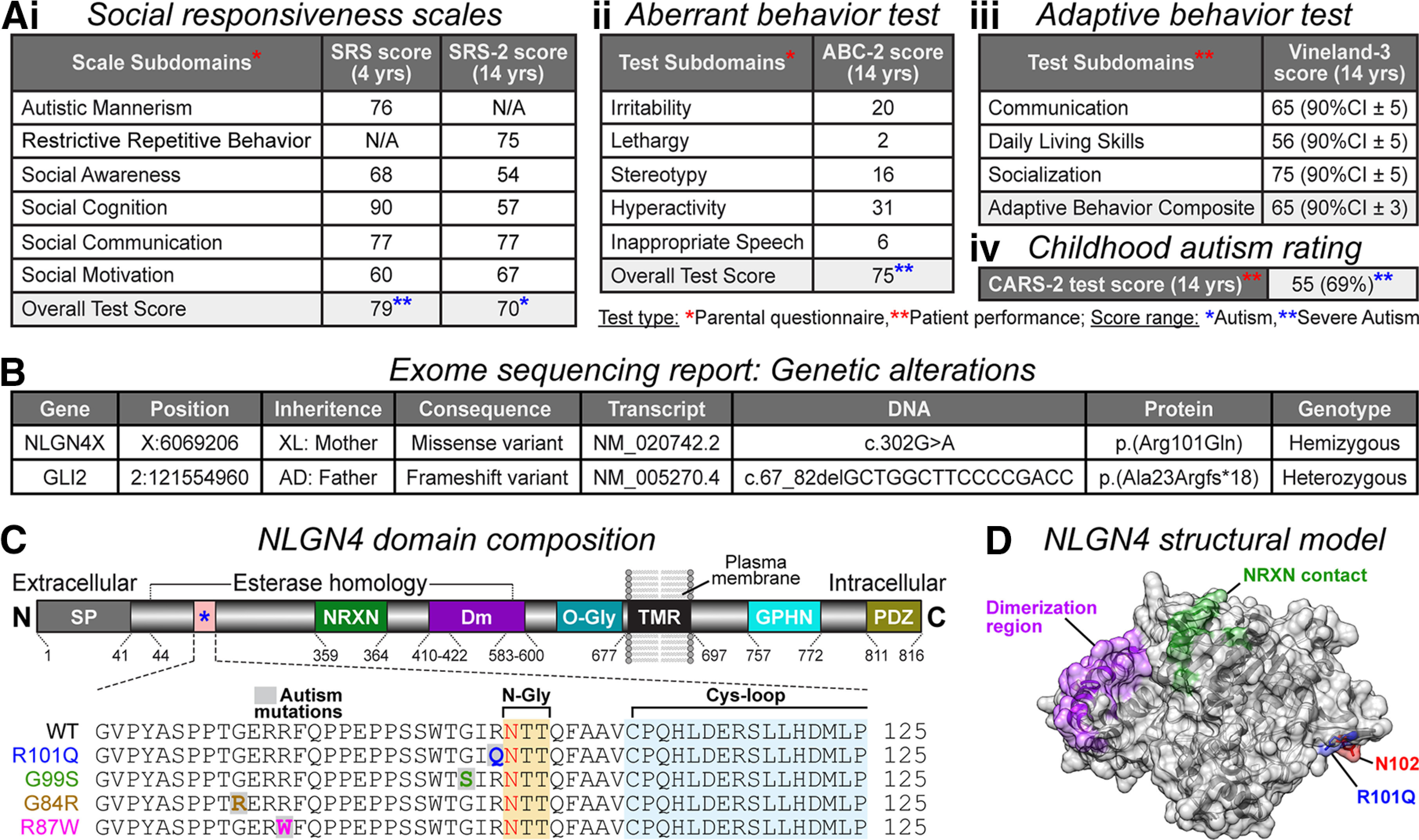
Identification of NLGN4 missense mutation in an autistic patient. Ai–iii, Behavior assessments leading to ASD diagnosis in the proband. Subdomain scores for social responsiveness tests (SRS and SRS-2, respectively conducted at ages 4 and 14 years using parental questionnaire; severe autism score, ≥76, moderate autism score, 66–75; mild deficit score, 60–65; Constantino, 2005; Constantino and Gruber, 2012; i), aberrant behavior checklist (ABC-2 test performed at age 14 years using the parental questionnaire; severe autism score, 75; Aman and Singh, 2017; ii), adaptive behavior scales (Vineland-3 assessment at age 14 years via professional observation; results are represented as 90% confidence interval ± SD; below-average score, <100; Sparrow et al., 2016; iii), and childhood autism rating (CARS-2 test at age 14 years via professional observation; severe autism score, ≥35; Schopler and Van Bourgondien, 2010; iv). B, WES report listing genetic alterations in NLGN4X and GLI2. Sequencing shows that the patient is hemizygous for a maternally inherited missense mutation in the NLGN4X gene, producing the Arg101Gln (R101Q) protein variant. The GLI2 heterozygous mutation originated from an asymptomatic father. C, Annotated map of NLGN4 with domain composition and corresponding amino acid numbers (top, not to scale): signal peptide (SP; gray), NRXN-binding domain (NRXN; green), dimerization residues (Dm; purple), O-glycosylation site (O-Gly; teal), transmembrane region (TMR; black), Gephyrin-binding domain (GPHN; cyan), and PDZ-binding sequence (PDZ; gold). The R101Q mutation is located within the esterase homology domain of NLGN4 (bottom, magnified view), neighboring a consensus site for N-linked glycosylation (N-Gly; yellow), and proximal to a cysteine-loop structure (Cys-loop; blue). The R101Q variant is also adjacent to previously reported ASD mutations (e.g., G99S, G84R, and R87W). D, Model of NLGN4 extracellular domain indicating spatial orientation of the R101Q mutation (blue), proximal to N-glycosylation (red) residue, and distal from dimerization (purple) and NRXN-contacting (green) regions.
