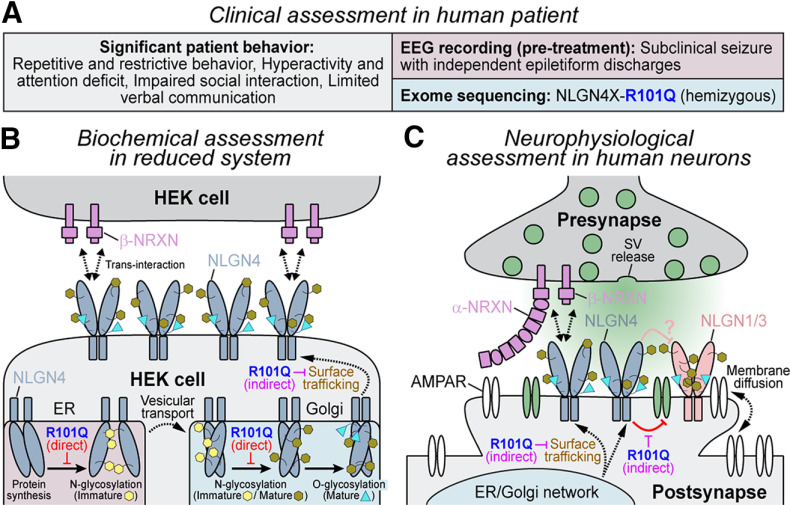
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of NLGN4 R101Q mutation-induced defects in cellular models. A, Summary of clinical evaluations performed on an autistic patient carrying R101Q substitution in NLGN4. B, In HEK cells, R101Q mutation directly impairs N-linked glycosylation of NLGN4, increases its accumulation in ER and Golgi, and, as a result, indirectly decreases its surface trafficking to the cell membrane. C, In stem cell -derived human neurons, R101Q mutation-mediated reduction in surface trafficking relieves NLGN4-induced inhibition of AMPAR clustering at the excitatory postsynapses, and thus enhances neuronal excitability.