Fig. 6. Dabrafenib and AZD5438 posttreatment protect against noise-mediated hearing loss in adult mice.
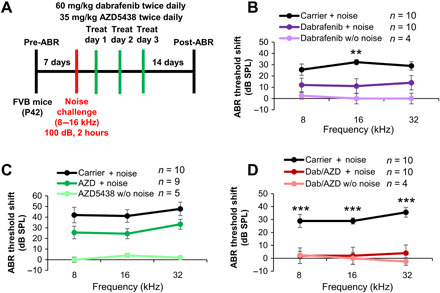
(A) Schedule of administration of compound and noise exposure to adult P42 FVB mice. (B) ABR threshold shifts recorded 14 days after 100-dB 8- to 16-kHz octave band noise for 2 hours for control and dabrafenib (60 kg/mg) twice daily treated mice by oral gavage. Dabrafenib treatment without noise exposure (light purple), noise alone (black), and dabrafenib treatment with noise exposure (dark purple). Means ± SEM, **P < 0.01 compared to noise alone by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (C) ABR threshold shifts recorded 14 days after 100-dB 8- to 16-kHz octave band noise for 2 hours for control and AZD5438 (35 kg/mg) twice daily treated mice by oral gavage. AZD5438 treatment without noise exposure (light green), noise alone (black), and dabrafenib treatment with noise exposure (dark green). The values were not significant compared to noise alone by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (D) ABR threshold shifts recorded 14 days after 100-dB 8- to 16-kHz octave band noise for 2 hours for control and combined dabrafenib (60 kg/mg) and AZD5438 (35 mg/kg) twice daily treated mice by oral gavage. Dabrafenib and AZD5438 treatment without noise exposure (light red), noise alone (black), dabrafenib, and AZD5438 treatment (dark red). Means ± SEM, ***P < 0.001 compared to noise alone by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test.
