Fig. 3. Chemical characterization of bile salt particles fabricated with the gold-assisted bulk templating method.
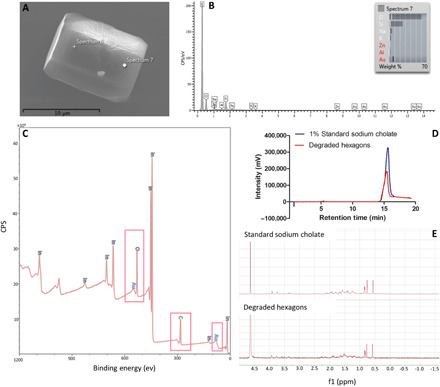
(A) SEM image of the product of the fabrication process. (B) EDS analysis of cholate-based hexagons. The presence of silicon and other elements in the spectrum is the result of drying the sample on a glass slide. (C) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis on the dried cholate hexagons mounted on indium foil, where CPS represents counts per second. Colored elemental labeling is added to the data, and pink boxes are drawn around the carbon, oxygen, and gold peaks to make the data more comprehensible. (D) High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis on the degradation products of hexagons (red peak) and standard sodium cholate solution (purple peak) in a 50:50 mixture of acetonitrile and water. (E) Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum of 3% standard sodium cholate (top) and the degradation products of cholate-based hexagons (bottom) in deuterated water. The high-intensity peak showing up at 4.6 ppm is the solvent peak. The intensity of the peaks for degraded hexagons is increased using the MestReNova software to make the comparison between the two spectrums easier.
