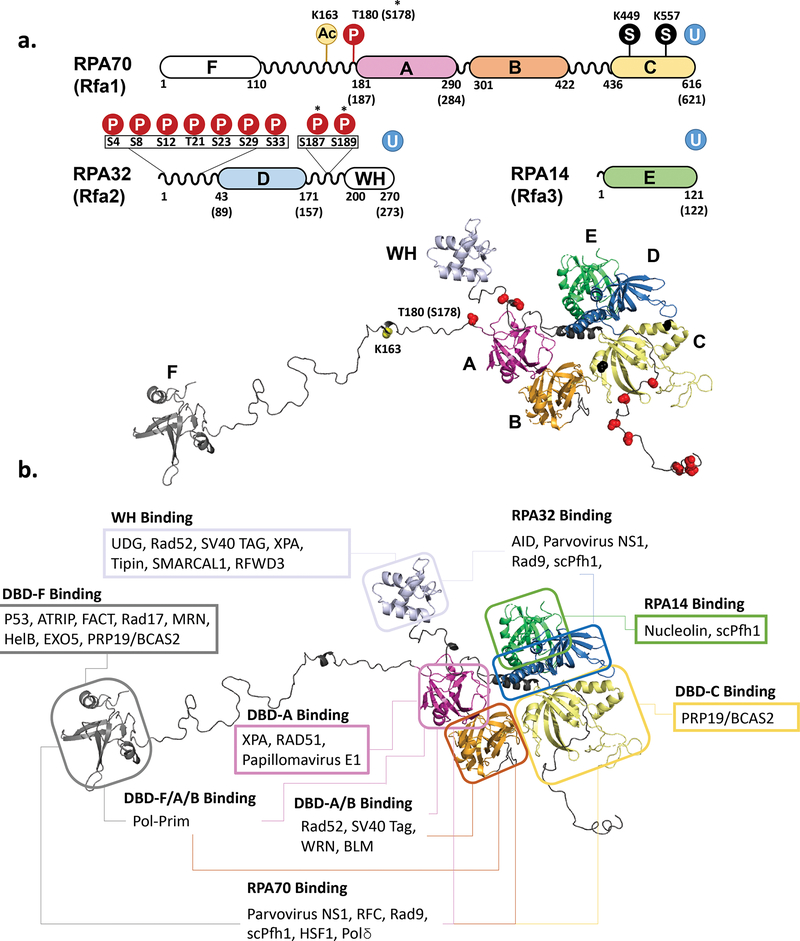
Figure 7. Protein-protein interaction and posttranslational modifications involving RPA.
(a) Schematic representation of the RPA primary structure with sites of posttranslational modifications and the same modifications mapped on the model of human RPA. Phosphorylation sites are marked with a P in a red circle and with the amino acid noted. SUMOylation sites are marked with an S in a black circle. Ubiquitinylation (U in a blue circle) has been identified on each of the RPA subunits, though specific site are not noted. *Asterisks note phosphorylation sites that were found in yeast RPA. S187/189 have only been noted in yeast. T180 is the corresponding site in human RPA that was identified as S187 in yeast. (b) Sites of Protein-Protein interactions mapped on the structural model of human RPA. Each box is labeled with the location on the RPA molecule that the listed proteins have been found to interact with. In the case of several proteins, multiple binding sites have been identified. While some proteins have only been tested for interaction with entire subunits of RPA, others have been found to bind to specific portions of a subunit, in which case the protein in only noted in the most specific region instead of the subunit. Table 2 indicates the specific amino acid regions where it is known.