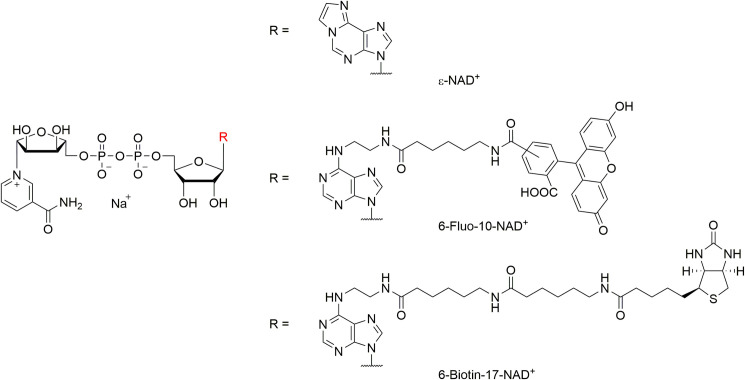
Fig 1. Molecular structures of NAD+-analogues used in this study.
The fluorescent properties of the NAD+ analogues employed here are established via the additional etheno-function bridging the N6- and 1-position (ε-NAD+) or via the fluorescent dye fluorescein attached via a spacer of 10 bond lengths at the N6-position (6-Fluo-10-NAD+). 6-Biotin-17-NAD+ is not fluorescent itself, but features a biotin moiety, which is also attached to the N6-position (via a spacer of 17 bond lengths) and can be addressed by a fluorescent dye such as avidin-Alexa fluor488.