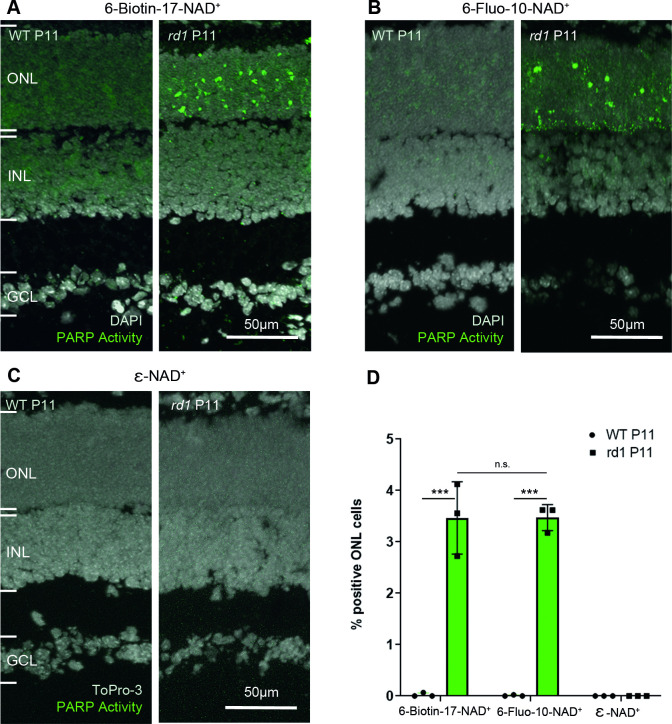
Fig 2. PARP activity detection with three different NAD+ analogues, in wild-type and rd1 retina.
Retinal tissue sections derived from either wild-type (WT) or rd1 animals, at post-natal (P) day 11, were incubated with different NAD+ analogues. (A) In the two-step assay, employing 6-Biotin-17-NAD+, PARP activity positive cells were rarely seen in the WT retina but readily detected in the rd1 outer nuclear layer (ONL). (B) The single-step assay with 6-Fluo-10-NAD+ detected similar numbers of PARP activity positive cells in the rd1 ONL. (C) No PARP activity was observable with the assay employing ε-NAD+ and a standard UV band-pass filter intended for DAPI visualization. (D) Quantification of PARP activity positive cells in WT and rd1 ONL in assays using the three different NAD+ analogues. DAPI was used as nuclear counterstaining in A and B; To-Pro-3 was used in C. PARP assays performed on tissue sections derived from at least three different WT and rd1 animals (n = 3); error bars indicate STD; statistical analysis: two-way ANOVA with multiple comparison. INL = inner nuclear layer, GCL = ganglion cell layer.