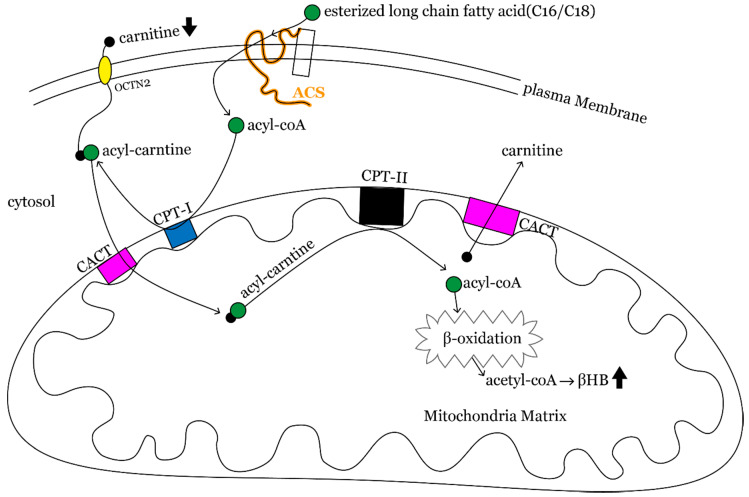
Figure 3.
Fatty acid β-oxidation pathway. Fatty acids (especially long-chain fatty acids) undergo acylation, a process catalyzed by acyl-CoA synthases that traps them in the cytoplasm as acyl-CoA thioesters. Acyl-CoA thioesters then conjugate to carnitine with formation of acylcarnitines through the action of carnitine palmitoyl transferase I. Acylcarnitines are translocated across the inner mitochondrial membrane by acylcarnitine translocase. Carnitine can be removed from acylcarnitine by carnitine palmitoyl transferase II inside the mitochondria, and acyl-CoAs are re-generated. Acyl-CoAs can enter β-oxidation in the mitochondrial matrix with final products of acetyl-CoA that produce ketone bodies (mainly βHB) in the liver.