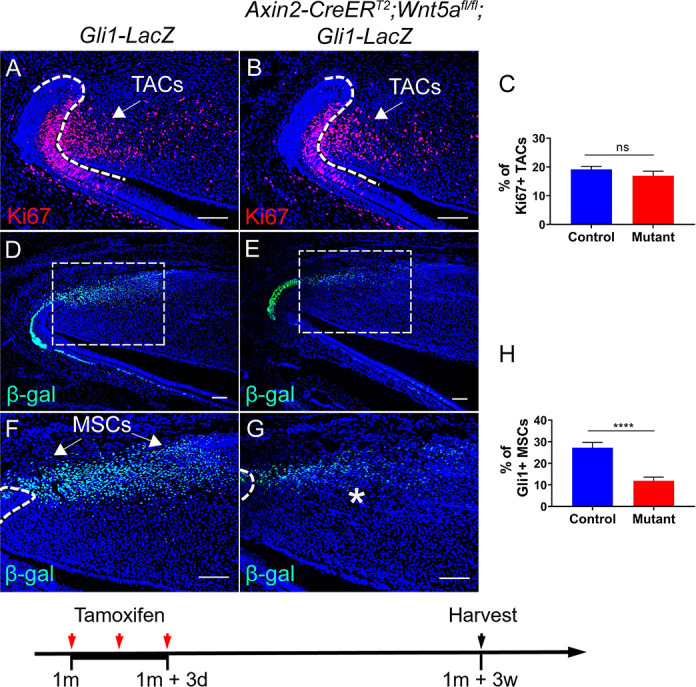
Figure 5. Loss of Wnt5a results in loss of Gli1+ mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
(A and B) Ki67 staining (red) of incisors from Gli1-LacZ (control) and Axin2-CreERT2;Wnt5afl/fl;Gli1-LacZ mice 3 weeks after tamoxifen induction. (C) Quantitation of the percentage of Ki67+ transit amplifying cells (TACs) from (A and B). (D–G) β-gal staining (green) of incisors from 1-month-old Gli1-LacZ and Axin2-CreERT2;Wnt5afl/fl;Gli1-LacZ mice 3 weeks after tamoxifen induction. Boxes in (D and E) are shown magnified in (F and G), respectively. (H) Quantitation of the percentage of Gli1+ cells per higher magnification section (F and G) of Gli1-LacZ and Axin2-CreERT2;Wnt5afl/fl;Gli1-LacZ incisor mesenchyme. Schematic at the bottom indicates induction protocol. The white dashed lines outline the cervical loop. Arrows indicate positive signal and asterisks indicate diminished signal. All quantitative data are presented as mean ± SD. ns, no significance. ****, p<0.0001. Four mice with four sections within each mouse per group were used to quantify Ki67+ cells. Gli1+ cells in the proximal region between the two cervical loops were counted in the mouse incisor. Scale bars, 100 μm.