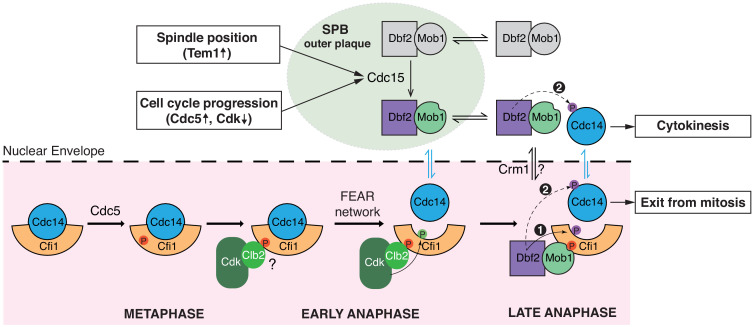
Figure 7. A model for Cdc14 activation and mitotic exit in budding yeast.
In metaphase, Cdc5 phosphorylates Cfi1/Net1 in the nucleolus to prepare for Cdc14 release/activation in anaphase. Upon anaphase onset, the Cdc fourteen early anaphase release (FEAR) network promotes phosphorylation of Cfi1/Net1 by Clb2-Cdk1 which results in transient release of Cdc14 from the nucleolus. In the meantime, the mitotic exit etwork (MEN) kinase Cdc15 is activated by integrating inputs from both spindle position (via Tem1) and cell cycle progression (via Cdc5 and CDK activities). Activated (spindle pole body [SPB]-localized) Cdc15 phosphorylates the SPB outer plaque protein Nud1 which creates a dynamic docking site for the MEN terminal kinase complex Dbf2-Mob1 and facilitates phosphorylation and activation of Dbf2-Mob1 by Cdc15. Activated Dbf2-Mob1 gains access to the nucleus and is targeted to the nucleolus by interacting with Cdc5-primed Cfi1/Net1. Nucleolar Dbf2-Mob1 then phosphorylates Cfi1/Net1, keeping Cdc14 dissociated from its nucleolar inhibitor to trigger exit from mitosis. In addition, active Dbf2-Mob1 in the nucleolus and/or cytoplasm phosphorylates Cdc14 at its nuclear localization signal (NLS) resulting in cytoplasmic retention of Cdc14 to facilitate cytokinesis.