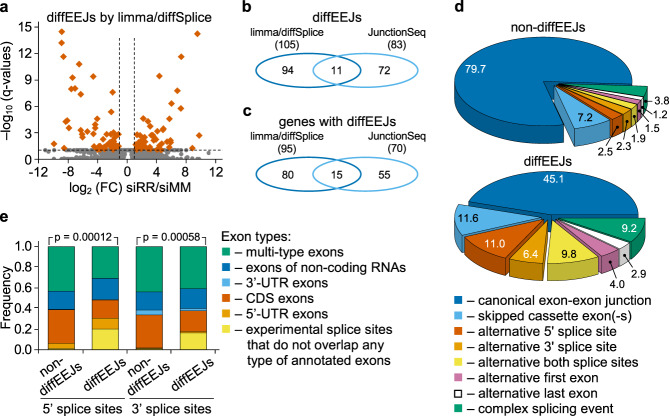
Fig. 2. Knockdown of RUNX1/RUNX1T1 causes changes in exon-exon linkages in leukemic cells.
a Vulcano plot showing differential splicing of exons identified by limma/diffSplice algorithm. Orange rhombi indicated differentially used exon-exon junctions (diffEEJs) with more than 2-fold change and q < 0.1. b Venn diagramme showing the overlap between diffEEJs identified by limma/diffSplice and JunctionSeq algorithms. c Venn diagramme showing overlap of genes with diffUEs identified by limma/diffSplice and JunctionSeq algorithms. d Pie charts showing the classification of diffEEJs and non-differential exon-exon junctions (non-diffEEJs) according to the modes of alternative splicing. Numbers indicate the percentage of splicing events assigned to a particular mode of splicing. Complex splicing means several (two or more) alternative splicing events occurred simultaneously. e Distribution of the splice sites with diffEEJs and non-diffEEJs among the various functional types of exons. P-values were calculated with χ2 test. Panels a to e are based on data from Kasumi-1 cells.