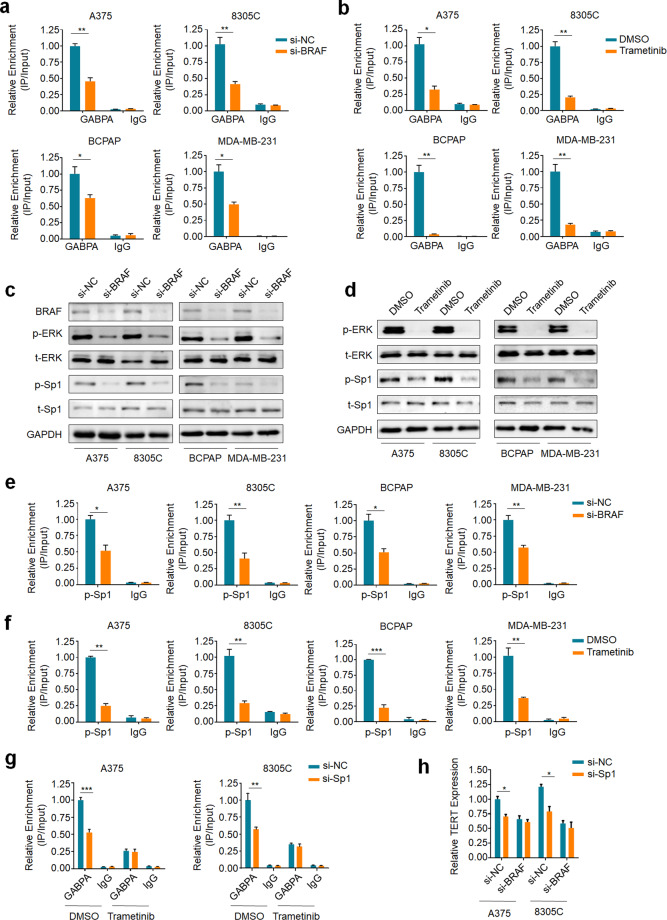
Fig. 2. The BRAFV600E/ERK/Sp1 signaling enhances the recruitment of GABPA to mutant TERT promoter.
ChIP-qPCR assay was performed in the indicated cells to evaluate the effect of inhibition of ERK activation by BRAF knockdown (a) or trametinib treatment (b) on the binding of GABPA to mutant TERT promoter. Western blot analysis was performed in the indicated cells to evaluate the effect of BRAF knockdown (c) or trametinib treatment (d) on phosphorylation of ERK and Sp1. GAPDH was used as a loading control. ChIP-qPCR assay was performed in the indicated cells to test the effect of BRAF knockdown (e) or trametinib treatment (f) on the binding of p-Sp1 to mutant TERT promoter. g ChIP-qPCR assay was performed to determine the effect of Sp1 knockdown on the recruitment of GABPA to mutant TERT promoter in the indicated cells treated with trametinib or si-HDAC1. h qRT-PCR assay was performed to determine the effect of Sp1 knockdown on TERT expression in the indicated cells knocking down BRAF or control cells. 18S rRNA was used as a reference gene. Data were shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.