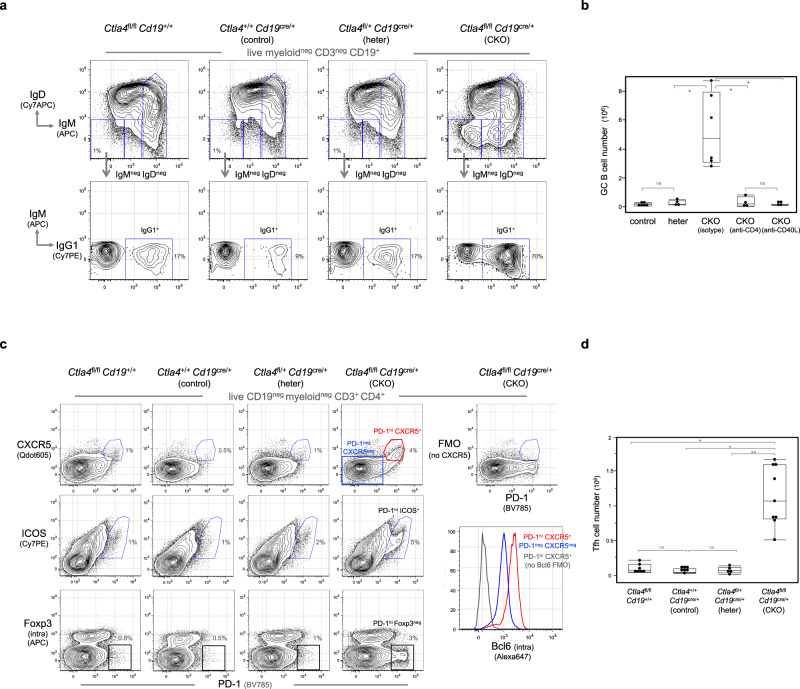
Fig. 3. T-dependent GC responses and Tfh cells arise spontaneously in spleens of CKO mice.
a Spleen cells from indicated mice were analyzed by FACS. Live myeloidneg CD3neg CD19+ splenic B cells were gated to show IgMneg IgDneg B cells, which were further gated to reveal IgG1+ cells. b Data summarizing the numbers of GC B cells (CD19+ CD38neg CD95+) in spleens of control, heterozygous and CKO mice treated with indicated antibodies is shown. Each dot represents data for an individual mouse, n = 4–6 mice per mouse group. *p < 0.01, ns, not significant (p < 0.1), nonparametric Wilcoxon one-way test. c Live myeloidneg CD19neg CD3+ CD4+ splenic T cells from indicated mice were gated to show PD-1, CXCR5, ICOS, and intracellular Foxp3 expression. Fluorescent minus one (FMO) staining, in which the fluorescent anti-CXCR5 antibody was omitted from the staining cocktail, is used to define CXCR5-expressing cells. FACS histogram on the right shows the intracellular Bcl6 expression by Tfh (PD-1hi CXCR5+, red line) and non-Tfh cells (PD-1neg CXCR5neg, blue line) in CKO mice. d Data summarizing numbers of Tfh cells (CD3+ CD4+ PD-1hi CXCR5+) in spleens of each mouse group is shown, n = 5–9 mice per mouse group, *p < 0.001, **p < 0.003, ns, not significant (p < 0.1), All mice are 2–3 months old. Box plots in c, b: box draws 75% (upper), 50% (center line), and 25% (down) quartile, the maxima and minima outliers are shown as top and bottom line, respectively.