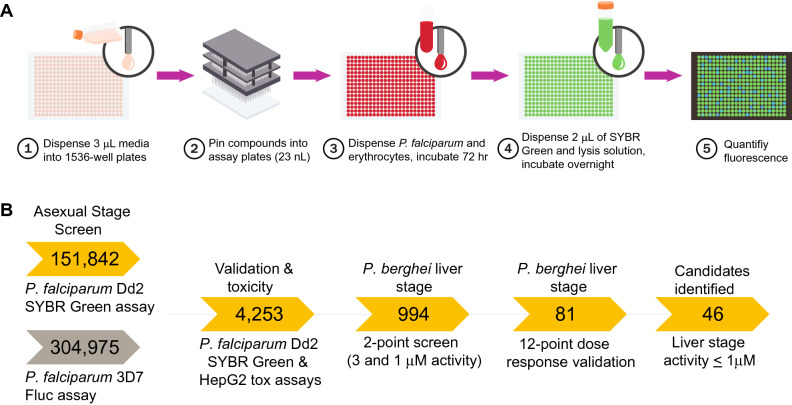
Figure 1.
Implementation of a quantitative high-throughput (qHTS) screen against P. falciparum asexual blood stage parasites. (A) Overview of qHTS primary and secondary screens of compound libraries assayed against P. falciparum ABS parasites cultured in human RBCs. In our second major screen, growth inhibition was monitored via quantification of SYBR Green fluorescence, which detects parasite DNA in human DNA-deficient RBCs. Alternatively, inhibition of parasite proliferation was quantified by measuring luciferase activity (not shown). (B) Screening pipeline for identifying candidate causal chemoprophylactic antimalarials. Two large qHTS campaigns used either SYBR Green or luciferase to test for inhibition of parasite growth, assaying a combined total of 456,817 compounds. Following qHTS, manual triage selected 4253 synthetically tractable compounds for validation of antiplasmodial activity and mammalian toxicity. Compounds were then evaluated in vitro against P. berghei liver stage parasites at 3 μM and 1 μM concentrations. Selected compounds were further evaluated in a 12-point dose–response against P. berghei liver stage parasites, yielding 46 with submicromolar AC50 values.