Figure 4.
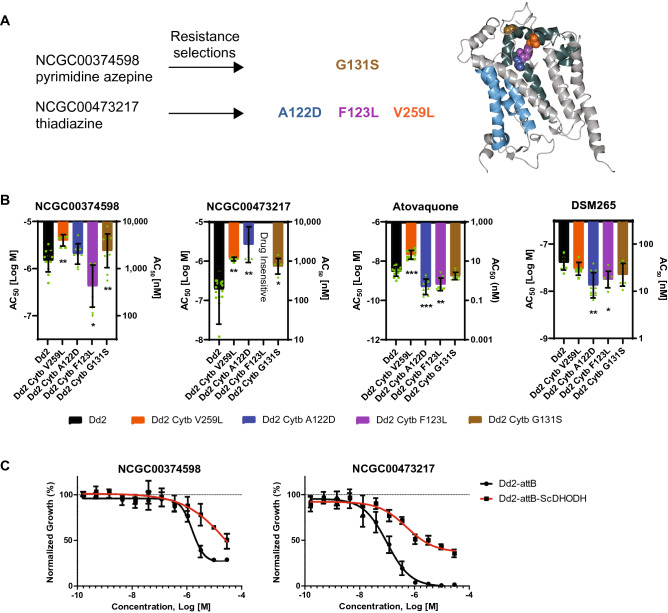
Resistance to pyrimidine azepine and thiadiazine hit compounds results in mutations in P. falciparum cytochrome b. (A) Resistance selection studies (left) with the pyrimidine azepine NCGC00374598 and the thiadiazine NCGC00473217 result in several cytochrome b mutations. Ribbon model (right) of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cytochrome b subunit, generated using CCP4mg78 (version 2.10, CCP4 Molecular Graphics; https://www.ccp4.ac.uk/MG/index.html). The positions homologous to the mutations found in this study (colored spheres) cluster within or near the quinone oxidation site Qo (green76), and are distal to the quinone reduction site Qi (light blue77). Cytochrome b subunits form a dimer within the multi-component cytochrome bc1 complex, a mitochondrial integral membrane protein complex required for mitochondrial respiration79. (B) Comparative activity of the lead compounds NCGC00374598 and NCGC00473217 against P. falciparum Dd2 (B2 clone; black) and drug-selected resistant isolates (V259L (orange), A122D (blue) and F123L (purple) cytochrome b mutants were selected under NCGC00473217 pressure; cytochrome b G131S (brown) was selected under NCGC00374598 pressure). The F123L variant showed no susceptibility to NCGC00473217 up to the highest concentration tested (− 4.54 Log [M] or 29 µM). Also shown are the susceptibility responses to atovaquone, a clinically used antimalarial that targets cytochrome b and DSM265 a clinical candidate that targets the parasite dihydroorotate dehydrogenase enzyme. The y-axis denotes the AC50 value (shown as mean ± SD) in Log molar concentration (left axis). The right y-axis shows the AC50 value in nanomolar concentration. Responses to chloroquine, amodiaquine, mefloquine, ELQ-300 and artemether were similar across all parasite lines (Supplementary Table 6). Statistical variance of AC50 compared to Dd2 (clone B2) parental line by Student’s t-test; p < 0.05, *; p < 0.01, **; p < 0.001, ***. (C) P. falciparum parasite asexual response to NCGC00374598 or NCGC00473217 in the transgenic Dd2 strain expressing the S. cerevisiae dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (Dd2-attB-ScDHODH), which confers resistance to mETC and DHODH inhibitors, or the transgenic parental line Dd2-attB.