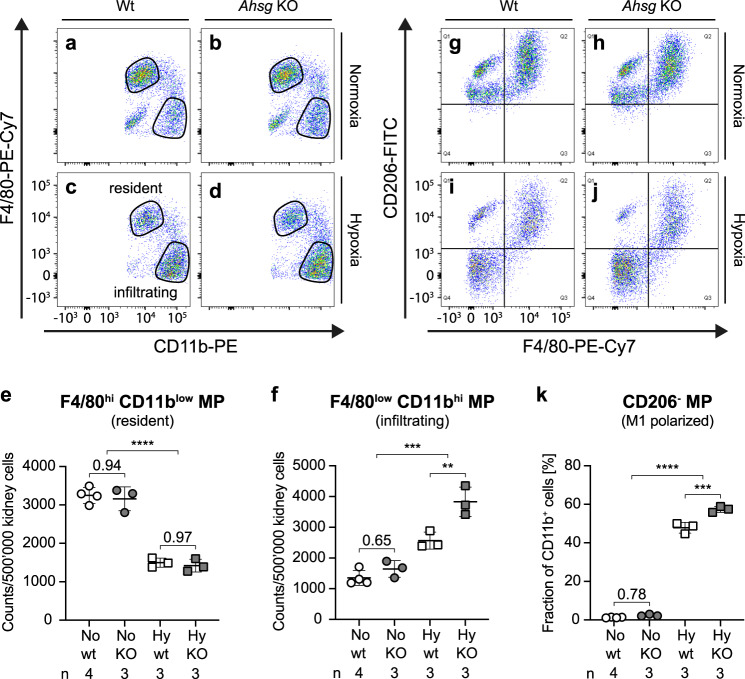
Fig. 7. Fetuin-A mitigates infiltration and polarization of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages.
a–d Under normoxic conditions (a, b), the majority of renal macrophages exhibits a F4/80hiCD11blow phenotype, indicating resident macrophages. The number of these cells was generally reduced under hypoxic conditions. Under hypoxic conditions (c, d), the cell count of infiltrating macrophages (F4/80lowCd11bhi) was increased. Lack of fetuin-A even more stimulated the infiltration of macrophages into hypoxic fetal kidneys (d). Images are representative of 3 (b–d) or 4 (a) sorted kidneys. e Quantification of resident macrophages shown in a–d. Unpaired two-tailed t-test (for comparison of normoxic and hypoxic condition). f Quantification of infiltrating macrophages shown in a–d. Unpaired two-tailed t-test with Welch’s correction (for comparison of normoxic and hypoxic condition). g–j Under normoxic conditions (g, h), the majority of renal macrophages exhibits a M2 CD206+ anti-inflammatory phenotype (depicted in the upper two quadrants). Hypoxic conditions (i, j) promoted the polarization of M1 CD206− pro-inflammatory macrophages (depicted in the lower two quadrants). This polarization is even more pronounced in fetal kidneys of Ahsg KO mice (j). Images are representative of three (h–j) or four (g) sorted kidneys. k Quantification of the lower two quadrants (CD206− macrophages) of the FACS blots shown in g–j. Unpaired two-tailed t-test with Welch’s correction (for comparison of normoxic and hypoxic condition). Data were analyzed from N = fetal kidneys and are presented as mean ± SEM (e, f, k). Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (e, f, k). Individual P-values are denoted above the comparison lines (e, f, k). (****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.