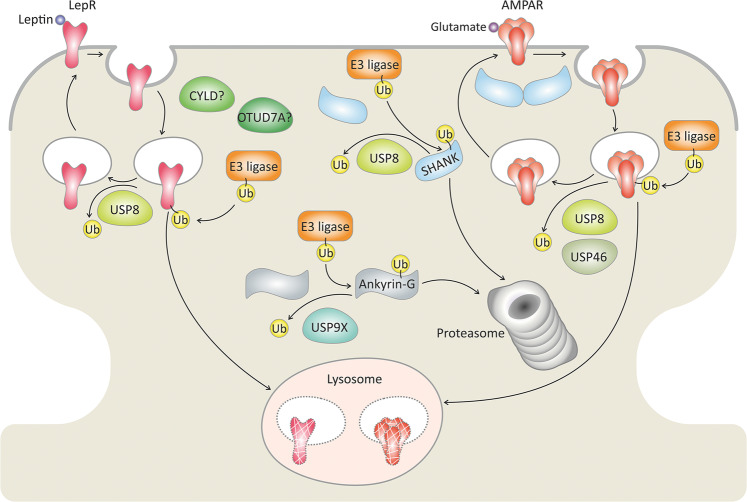
Fig. 2. An emerging model for DUB regulation of synaptic plasticity.
Activation of postsynaptic glutamate receptors controls neuron excitability. The postsynaptic density is enriched with a growing number of DUBs that antagonize E3-ligases and remove ubiquitin (Ub) chains, thereby protecting designated substrates from degradation by the lysosomes or the proteasome. Certain DUBs regulate the degradation and surface localization of the glutamate receptor, AMPAR. Moreover, a number of DUBs support the formation and function of the glutamatergic synapse by regulating the levels of scaffold proteins (SHANK and Ankyrin) and the leptin receptor (LepR). DUBs with yet unknown substrates are labeled with a question mark (?). The Ub symbol in this image indicates a polyubiquitin chain.