FIGURE 1.
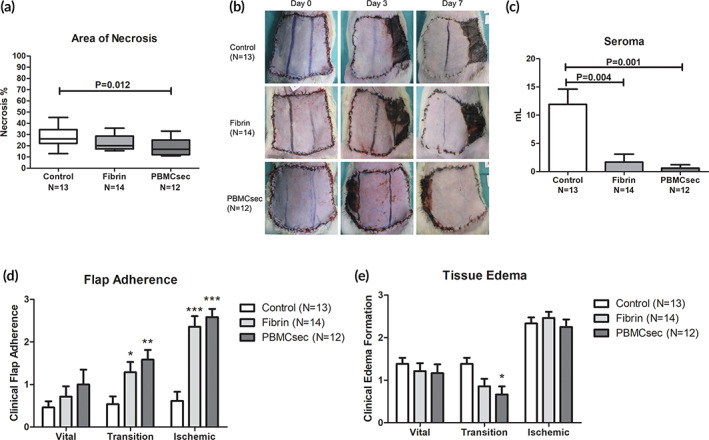
(a) The tissue necrosis rate was significantly reduced after a single, intraoperative application of the secretome derived from γ‐irradiated PBMCs (PBMCsec). Only the combinatory use of fibrin and PBMCsec showed significantly improved results. (b) Examples for the development of tissue necrosis over the postoperative period are shown for each group. (c) Seroma formation was evaluated on postoperative day 7. The use of fibrin sealant alone or in combination with PBMCsec significantly reduced the volume of seroma found in the surgical wounds. Results are given as mean ± SEM. (d) Flap adherence to the underlying tissue was evaluated clinically as parameter for tissue integration. Both groups, fibrin sealant alone and in combination with PBMC secretomes, showed markedly improved rates of flap adherence on postoperative day 7. (e) Tissue edema formation was comparable between all groups. However, in the transition zone of the flap, PBMCsec treatment led to significantly reduced clinical occurrence of edema 7 days after surgery. (*, <0.05 vs. control; **, <0.01 vs. control; ***, <0.001 vs. control)
