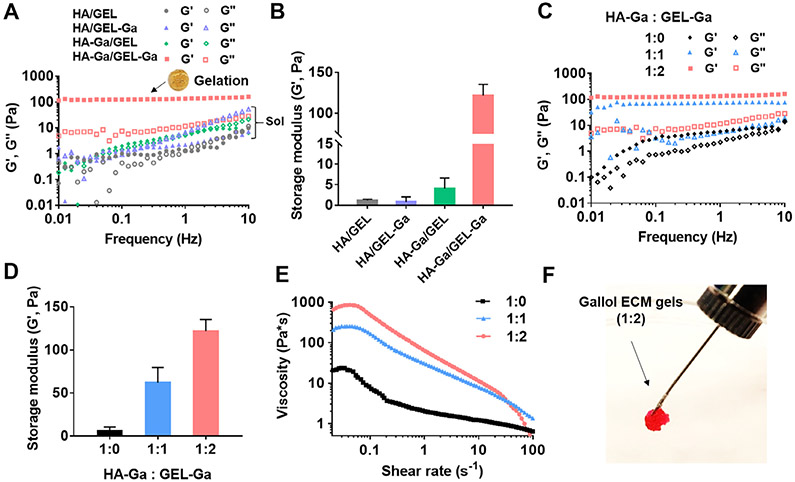
Fig. 2.
Mechanical characterization and extrusion of gallol ECM hydrogels immediately after mixing. (A) Frequency sweep (storage (G′) and loss (G″) moduli at 0.5% strain, 37 °C) and (B) G′ (1 Hz) of mixtures of non-gallol (hyaluronic acid (HA), gelatin (GEL)) and gallol (HA-Ga, GEL-Ga) polymers at 1:2 mass ratio and total concentration of 6 wt%. Gelation occurred only with the mixture of HA-Ga and GEL-Ga (inset photo of formed hydrogel). (C) Frequency sweep, (D) G′ (1 Hz), and (E) viscosity with increasing shear rate of the gallol ECM hydrogels with various HA-Ga:GEL-Ga mass ratios. (F) Macroscopic injectability of the rhodamine-containing gallol hydrogel (HA-Ga:GEL-Ga of 1:2) with a 25 G needle.