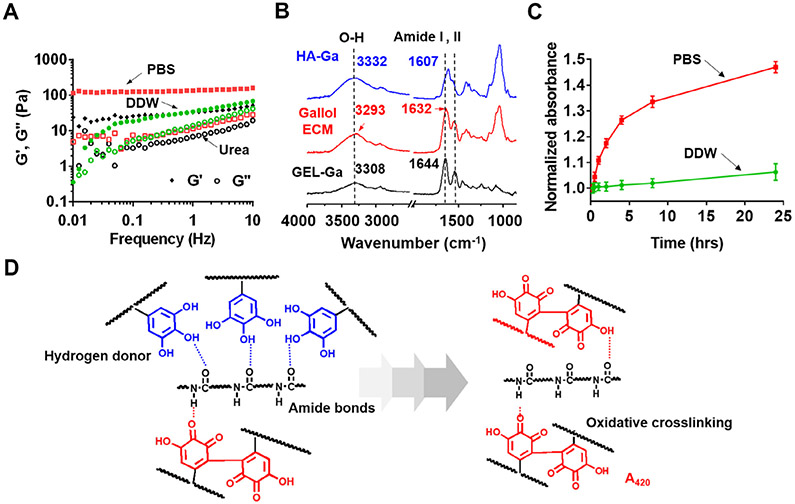
Fig. 4.
Physicochemical mechanism for the gallol ECM gelation. (A) Frequency sweep (storage (G′) and loss (G″) moduli at 0.5% strain, 37 °C) of gallol (HA-Ga, GEL-Ga) hydrogels at 1:2 mass ratio and 6 wt% formed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, red symbols) or with either deionized water (DDW, green symbols), or treatment of urea (1 M, black symbols). (B) ATR-IR spectra of the gallol ECM (red), HA-Ga alone (blue), and GEL-Ga alone (black). (C) Normalized (to values at 15 min) absorption (420 nm) of the gallol ECM mixtures prepared in PBS (red) or DDW (green) as a function of time. (D) Proposed gelation mechanism of temporally changing hydrogen bonds of the gallols with amide backbones (left panel, blue dashed line) to covalent crosslinking via gallol auto-oxidation (right panel, red compounds).