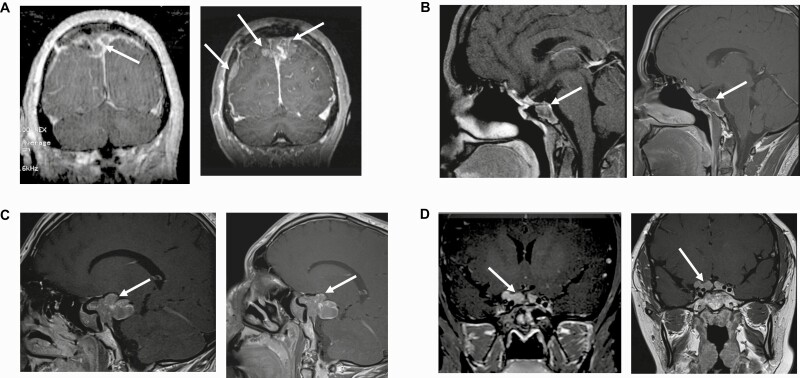
Figure 2.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at baseline and study end. A, MRI of patient 1 at (left) baseline and (right) study end. Baseline MRI demonstrates a parasagittal mass on the right side. Lesion measures 17 × 22 × 26 mm. MRI after 3 months of lapatinib therapy shows a 141% increase in tumor diameter now extending to the left. Lesion measures 36.7 × 27 × 41 mm. In addition, there is a new dural metastasis. B, MRI of patient 2 at (left) baseline and (right) study end. Baseline MRI demonstrates a heterogeneous lesion with ill-defined margins and adjacent normal structures. Note extension into the left sphenoid sinus, parasellar structures, anterior clinoid, and superior clivus. The infundibulum is midline to slightly deviated toward the left side. Optic chiasm is normal. Lesion measures 21.8 × 26.8 × 26.1 mm. MRI after 6 months of lapatinib therapy shows a 16.8% decrease in tumor diameter. Lesion measures 16.6 × 22.3 × 24.1 mm. C, MRI of patient 3 at (left) baseline and (right) study end. Baseline MRI demonstrates a large pituitary mass that expands downward, ventrally, superiorly, and posteriorly, including into the interpeduncular cistern and the right temporal fossa, and compressing the right optic nerve. There are areas of hemorrhage within the mass. Lesion measures 48 × 24.4 × 34.6 mm. MRI after 6 months of lapatinib therapy shows a 6% increase in tumor diameter on the right-sided posterior component. Lesion measures 50.9 × 26.6 × 35.1 mm. D, MRI of patient 4 at (left) baseline and (right) study end. Baseline MRI demonstrates a lobulated mass associated with the undersurface of the optic chiasm and extending into the bilateral suprasellar cisterns. Lesion measures 16.3 × 8.6 × 24.5 mm. MRI after 6 months of lapatinib therapy shows a 6.1% increase in tumor diameter in each dimension. Lesion measures 15.8 × 9.2 × 26 mm.