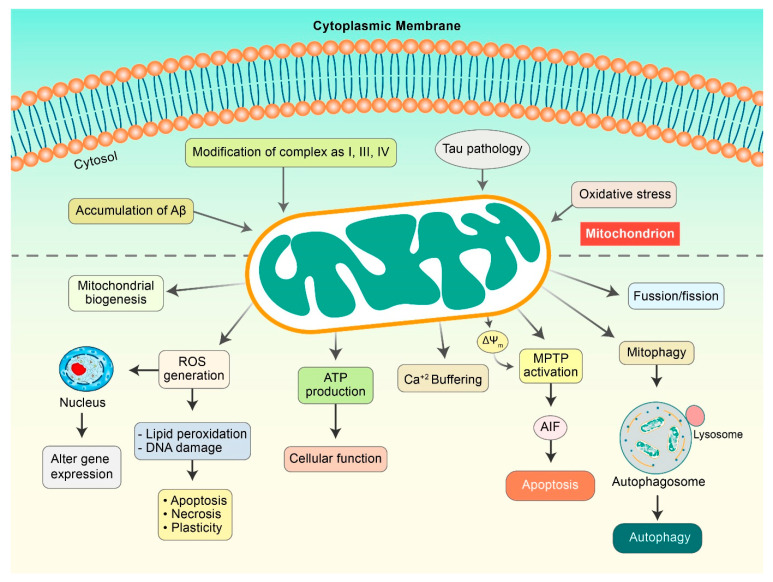
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial dysfunction in AD pathogenesis. Aβ and Tau initiate mitochondrial dysfunctions that can result in the modulation of several factors. ROS is generated, which causes lipid peroxidation and DNA damage to initiate apoptosis. Damaged mitochondria demonstrate a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) as a result of the activation of mitochondrial permeability transition pores (mPTPs), which release cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), and consequently, initiate apoptosis pathway. Aβ and pTau improve mitochondrial fission and mitophagy.