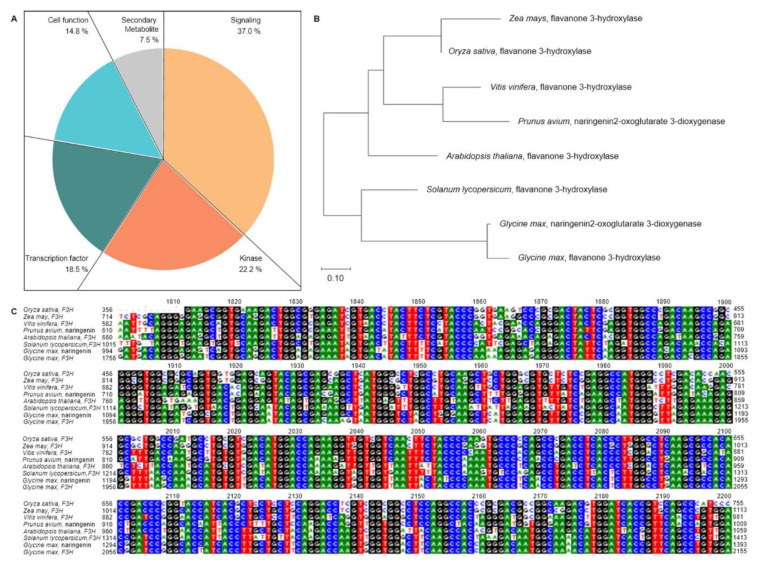
Figure 4.
Candidate gene distribution based on WBPH resistance-related QTL mapping phylogenetic tree of F3H. (A) Candidate genes associated with WBPH resistance included cell function, kinase, signaling, transcription factors, and secondary metabolites. Signaling was 37.0%, kinase was 22.2%, transcription factors were 18.5%, cell function was 14.8%, and secondary metabolites were 7.5%. (B) Comparison of homology between F3H of Oryza sativa (O. sativa) and F3H of A. thaliana, Z. mays, G. max, P. avium, S. lycopersicum, and V. vinifera. F3H of O. sativa was the most similar to F3H of Z. mays and showed a relatively high similarity to V. vinifera and P. avium. (C) Multiple sequence alignments of F3H. Comparison to the conserved nucleic acid sequences found in the F3H domain region of O. sativa, A. thaliana, Z. mays, G. max, P. avium, S. lycopersicum, and V. vinifera.