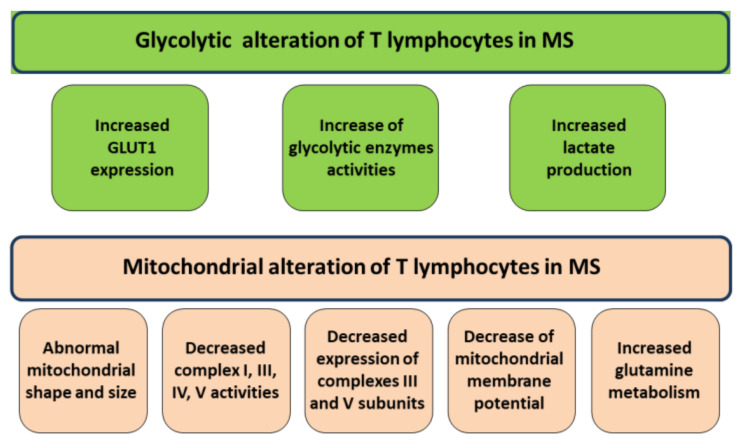
Figure 1.
Metabolic alterations of T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis (MS). Activated T cells metabolize large amounts of glucose associated with lactate production by increasing glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) expression at the plasma membrane [40]. In addition, to sustain cell proliferation, T cells also augments glutamine metabolism [35]. Mitochondria of T lymphocytes of MS patients show abnormal structure, decrease of oxidative phosphorylation system (OXPHOS) in term of subunit expression and complex activities and decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential [24,39,40,41].