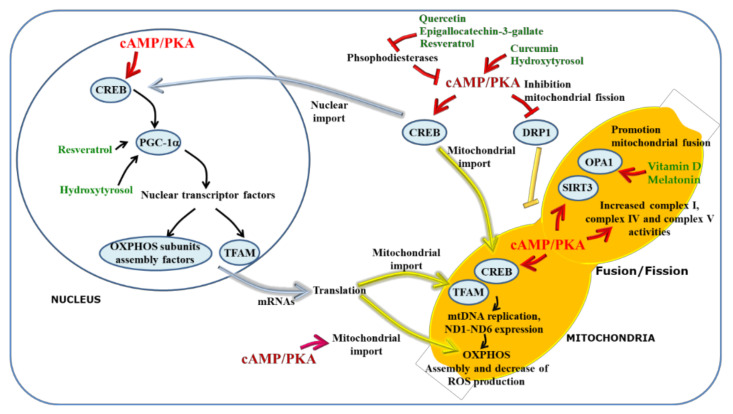
Figure 4.
Control by the cAMP pathway of mitochondria. PKA-dependent phosphorylation of CREB activates the PGC-1 alpha transcription cascade promoting the expression of nuclear genes coding for OXPHOS subunits and mitochondrial transcription factor (TFAM) [115]. In addition to the nucleus, CREB resides inside mitochondria, where it binds to the D-loop of mitochondrial DNA inducing expression of structural OXPHOS components [116,117]. PKA-dependent phosphorylation of the NDUFS4 subunit increases its import into mitochondria and assembly in complex I [118,119,120]. sAC-dependent cAMP production also promotes the complex I, IV and V activities [121,122,123,124]. PKA-dependent phosphorylation of DRP1, inhibits its pro-fission activity, thus promoting mitochondrial fusion and respiration [125,126]. sAC-dependent cAMP stabilizes SIRT3 expression and OPA1 proteolytic processing promoting mitochondrial fusion and resistance to apoptosis [95]. The nutraceutics are shown in green, closed to the target molecules, for details see the text. The cAMP/PKA pathway is shown in red, the nuclear protein transport in bluette and the mitochondrial protein import in yellow.