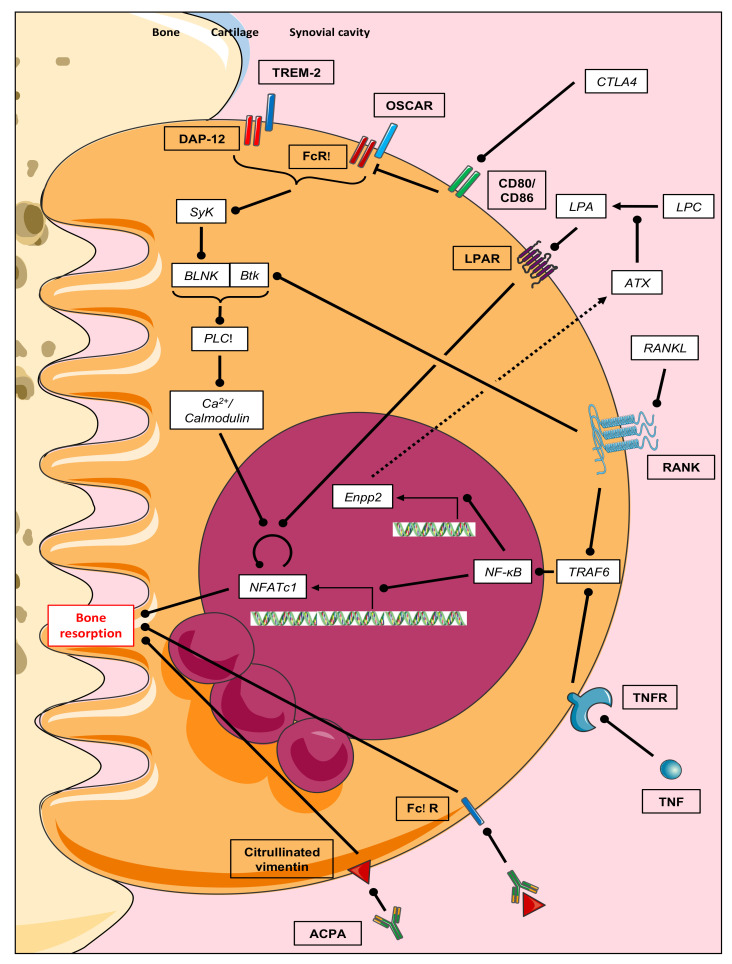
Figure 3.
Enhanced osteoclast bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis. Bone resorption is mediated by multiple pathways (RANKL/RANK, inflammatory cytokines, ITAM/Ca2+, and ATX/LPA) converging on NFATc1. Additionally, bone loss is mediated by direct and indirect ACPA-related mechanisms. ACPA: Anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies; ATX: Autotaxin; BLNK: B-cell linker protein; BtK: Burton tyrosine kinase; CD: Cluster of differentiation; CTLA4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; DAP-12: DNAX-activating protein of 12 kDa; Enpp2: Ectonucleotid pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2; FcγR: Fc gamma receptor; FcRγ: Fc receptor gamma subunit; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; IL: Interleukine; LPA: Lysophosphatidic acid; LPAR: LPA receptor; LPC: Lysophosphatidylcholine; MHC-1: Major histocompatibility complex 1; NFATc1: Nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1; NF-κb: Nuclear factor kappa B; OSCAR: Osteoclast associated receptor; PLCγ: Phospholipase C gamma; RANK: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B; RANKL: RANK ligand; Syk: Spleen tyrosine kinase; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TRAF6: TNF receptor-associated factor 6; TREM-2: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell. 2. Dashed triangle arrowheads: Secretion; simple triangle arrowheads: Chemical reaction; round arrowheads: Activation; flat arrowheads: Inhibition.