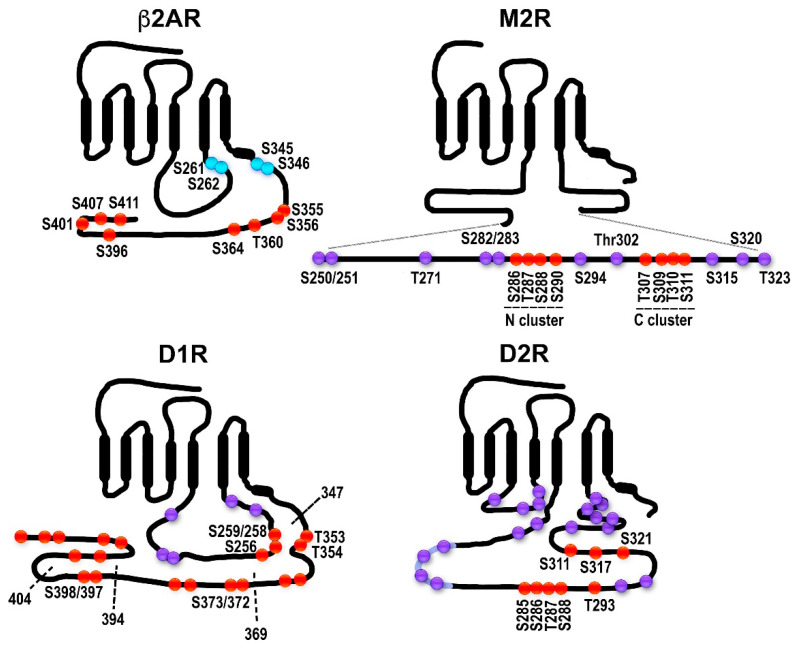
Figure 2.
Distribution of potential and established GRK phosphorylation sites in selected GPCRs. The classical model does not necessarily apply to all GPCRs: in some cases, receptor phosphorylation is not necessary or plays a minor role in arrestin binding; some arrestin-associated receptors do not internalize via coated pits; for others, arrestins appear to mediate receptor internalization, but not desensitization, etc. β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR). The sites in the human β2AR are shown. The sites of PKA phosphorylation are shown in blue. The sites of GRK phosphorylation are shown in red. All GRK targets are localized in the C-terminus, as in rhodopsin, β1AR, opioid and cannabinoid receptors, and many other GPCRs. Muscarinic M2 receptor (M2R). The sequence and GRK phosphorylation sites in the human M2R are shown. All putative sites are located in the 3rd cytoplasmic loop; the actual phosphorylation sites have been localized to the central part of the 3rd loop (Ser250-Thr323 shown here as an insert). The sites in the two characterized clusters are shown in red, the other sites in magenta. Two clusters of phosphorylatable residues (red) with different functions were described. Thr307-Ser311 (C cluster) appears to be necessary for desensitization; when the N cluster (residues Ser286-Ser290) is mutated to alanines, the receptor still desensitizes. Arrestin binding depends on the C-cluster [30]. Internalization is promoted by phosphorylation of either cluster [30,31,32]. Other potential phosphorylation sites within the region are shown in purple. Dopamine D1 receptor (D1R). D1R has sites in both the C-terminus and the 3rd cytoplasmic loop. The rat D1R is shown. The sites labeled in red have been shown to be phosphorylated in an agonist-dependent manner either in truncation experiments or via mutations to alanines [33]. Truncations used in [33] are shown as dotted lines with the last residue remaining labeled. Other potential phosphorylation sites are shown in purple. Dopamine D2 receptor (D2R). The rat D2R is shown. All phosphorylatable sites are in the 3rd cytoplasmic loop. Eight sites phosphorylated in an agonist-dependent manner by GRKs are shown in red [34]. Some of the other potential phosphorylation sites are shown in purple.