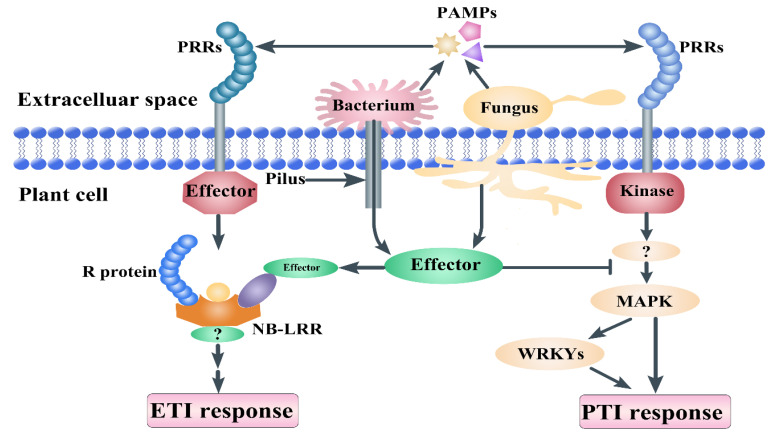
Figure 1.
Plant immunity principles. Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are molecules released from pathogens, such as chitin and flagellin. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) can recognize the PAMPs from the pathogens and transmit signals to mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and WRKY transcript factors, which induce PAMP-triggered immunity (PTI) response. Pilus is a tool that delivers bacterial effector proteins into the host cell. PRRs consist of the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain and are recognized by nucleotide-binding site (NB)-LRR receptors, which induce effector-triggered immunity (ETI). NB-LRR proteins consist of an LRR domain, a NB domain, and an amino-terminal Toll/interleukin-1 receptor resistance protein (TIR) or a coiled-coil (CC) domain.