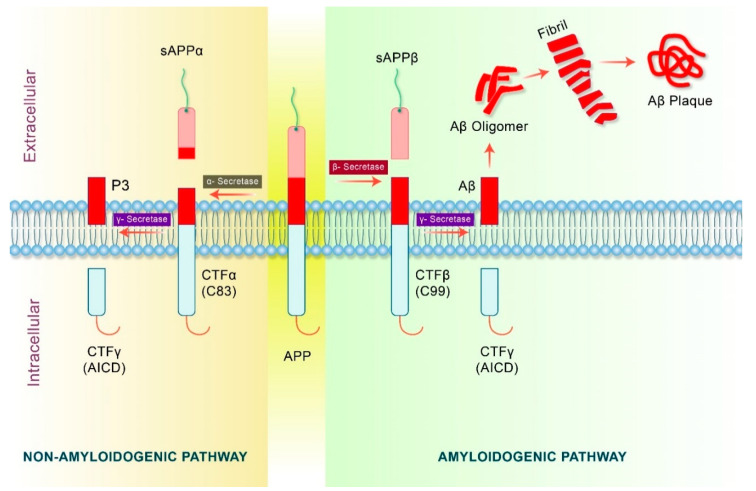
Figure 3.
APP processing pathways in AD. APP are generally processing in two different pathway, amyloidogenic and non-amyloidogenic. In the non-amyloidogenic pathway, APP is cleaved by α-secretase to form two fragments, an intracellular C-terminal fragment α (CTFα), C83, and an extracellular fragment, soluble amyloid precursor protein α (sAPPα). Cleavage of C83 fragment via γ-secretase yields a short peptide fragment, P3, and an APP intracellular domain (AICD). In the amyloidogenic pathway, APP is cleaved by β-secretase which produces a soluble amyloid precursor protein β (sAPP β) and a C-terminal fragment β (CTFβ) or C99 fragment. C99 fragment is cleaved by γ-secretase to produce Aβ and C-terminal fragment γ (CTFγ) or AICD. Aβ further forms Aβ oligomers which subsequently results in the formation of fibrils and neurotoxic Aβ plaques extracellularly.