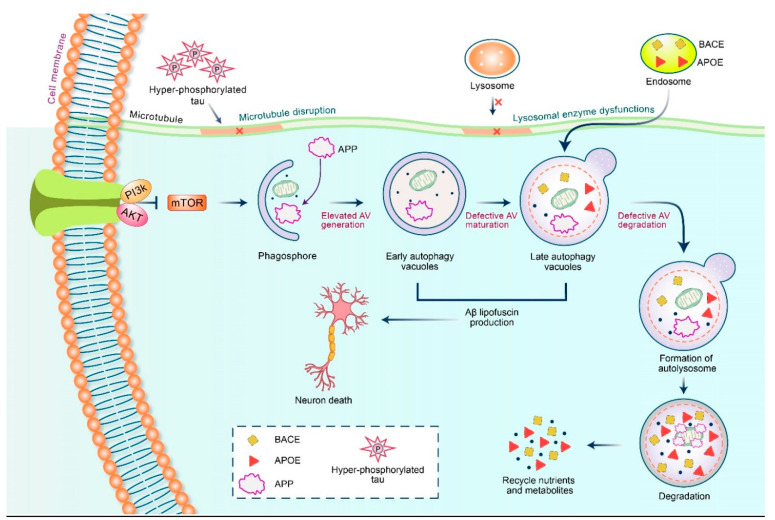
Figure 5.
APP, BACE, and ApoE are AD-related molecules and eliminated by autophagy. In the initial stage of AD, autophagic vacuoles (AVs) are formed due to the stress induced by APP mutants which ultimately damage the mitochondria. During the late stage of AD, maturation as well as degradation of autophagosomes are blocked by microtubule disruption which causes hyperphosphorylated tau accumulation. Tau hyperphosphorylation might inhibit microtubule assembly in addition to disrupt the preassembled microtubules. Eventually, dysfunction of lysosomal enzymes interferes with autophagosome-lysosome fusion in AD. Taken together, these defects of autophagy contribute to accumulation of AVs along with other AD-related molecules which increased intracellular Aβ deposition as well as lipofuscin thereby causing neuronal cell degeneration and death.