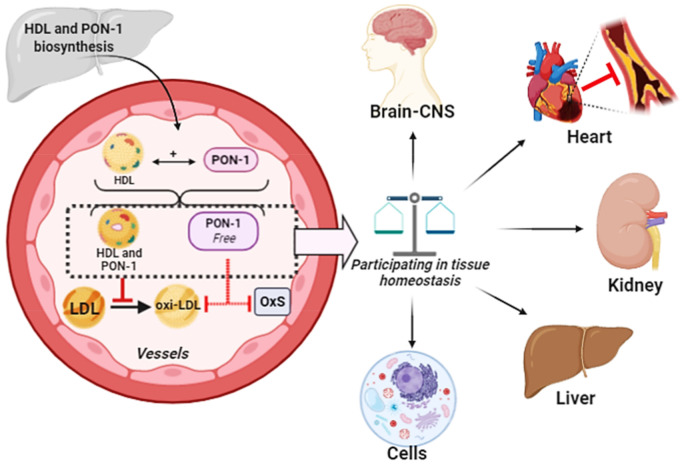
Figure 3.
HDL biosynthesis occurs in the liver and in a small part of the intestine. Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) biosynthesis occurs only in the liver. After the formation of both HDL and PON1, they enter into the circulation. An association between HDL and PON1 can occur both in the hepatic circulation (to a lesser extent) and in the plasma. A small amount is free PON1, which do not adhere to any lipoprotein. An important function of PON1 is to prevent oxidation of both HDL and LDL, through the hydrolysis of reactive compounds. Oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) is pro-inflammatory and atherogenic. PON1 is carried to the tissues by HDL, where it performs its function as an antioxidant enzyme. In addition, the portion of free PON1 in the plasma also acts as an antioxidant, but its hydrolysis capacity is reduced.