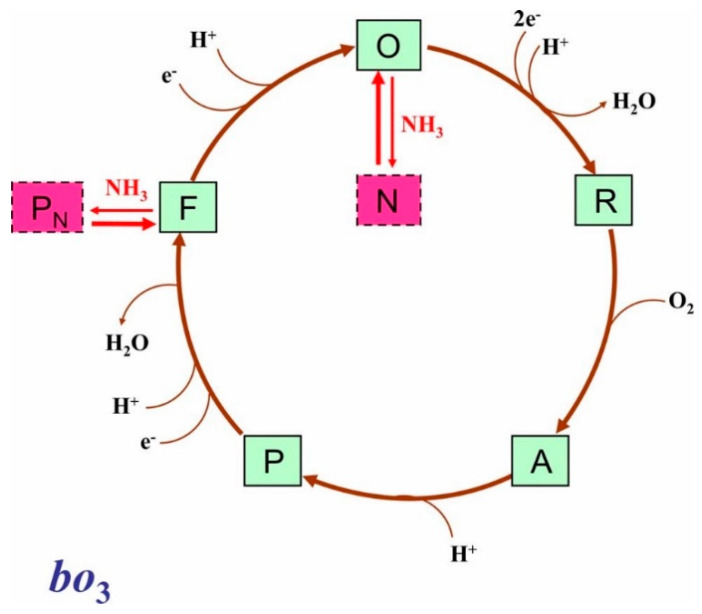
Figure 5.
The possible effect of ammonia on the catalytic cycle of cytochrome bo3. Proposed catalytic intermediates O (o33+–OH CuB2+), R (o32+ CuB+), A (o32+–O2 CuB+), P (o34+=O2− CuB2+–OH), and F (o34+=O2− CuB2+) are shown. Possible redox and ligation state of the binuclear site in each intermediate is indicated in brackets. Only chemical protons are shown. Pumped protons are not shown for clarity. The two ferryl species P and F likely differ in the presence of an aromatic amino acid radical in P, as in the intermediate PM of cytochrome c oxidase [66]. NH3 presumably converts F into the PN state (o34+=O2− CuB2+–NH3) and O into the ammonia complex N (o33+–NH2− CuB2+ and/or o33+– NH2− CuB2+–NH3), thereby leading to the inhibition of the oxidase activity.