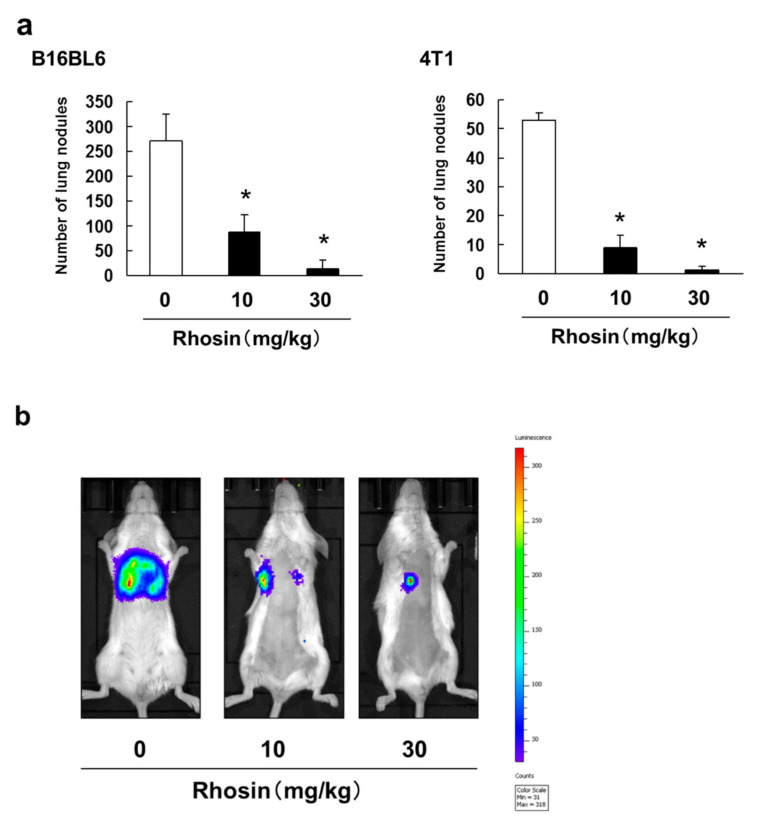
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effect of intraperitoneal administration of rhosin on lung metastasis. (a) B16BL6 cells (1 × 105 cells in 0.2 mL) and 4T1 cells (1 × 105 cells in 0.2 mL) were injected into the tail vein of syngeneic C57BL/6J mice and Balb/c mice. Mice were treated daily from days 1 to 14 with 10 or 30 mg/kg rhosin. After 14 days, visible nodules that had metastasized to the lungs were counted. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD for 10 mice. * p < 0.01 vs. the controls (0.1% DMSO-treated) (ANOVA with Dunnett’s test); (b) Representative mice injected with 4T1-luc cells (1 × 105 cells in 0.2 mL). Mice were treated daily from days 1 to 14 with 10 or 30 mg/kg rhosin. On day 14, tumor cells in mice were detected by IVIS Lumina XRMS Series III Imaging System.