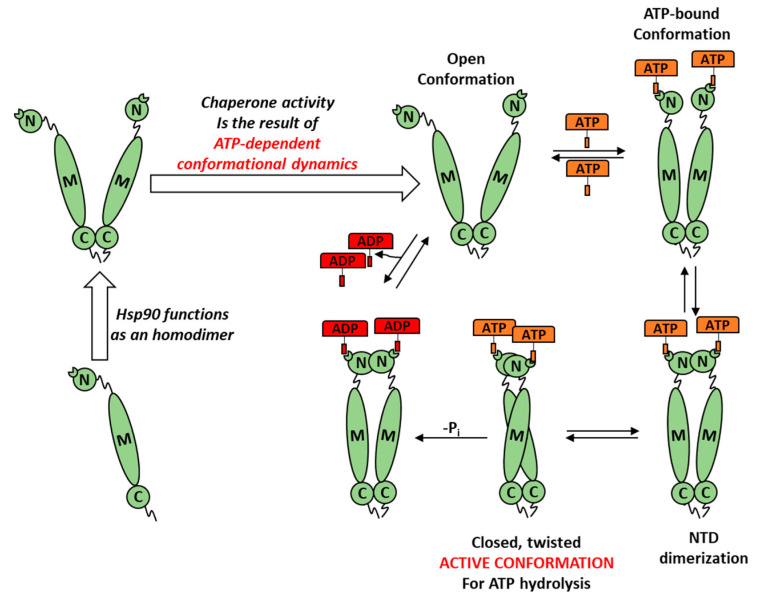
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the conformational dynamics characterizing a heat-shock chaperone. N = N terminus; C = C terminus and M = middle domain. ATP binding and its consequent hydrolysis modulates Hsp90 chaperone activity by regulating the transitions between conformational protein sub-states with distinct functional properties. The binding of allosteric ligands “selects” specific protein conformations via the modification of Hsp90 ATPase activity kinetics and the consequent interaction with client proteins [31].