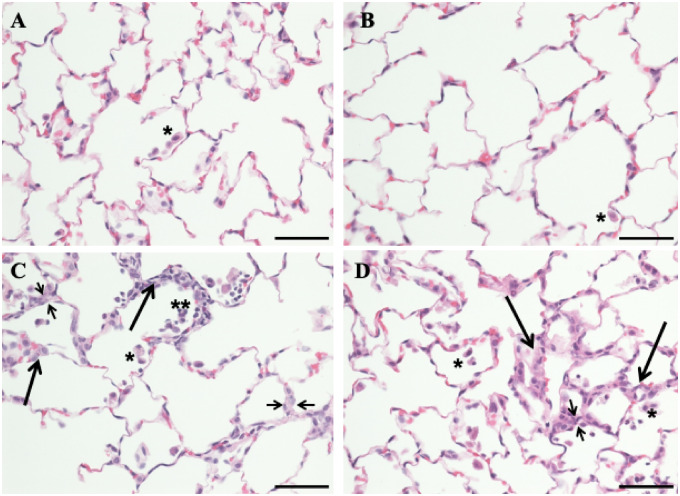
Figure 1.
Photomicrographs of lung sections from the control, tobacco smoke (TS)-, crystalline silica (CS)-, and TS plus CS-exposed rats. Rats were exposed to air, CS, TS, or TS plus CS as described in the text. Lung sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Normal pulmonary architecture with occasional intra-luminal alveolar macrophages (single asterisk) was noted in air alone-exposed (A) and TS alone-exposed animals (B). Rats exposed to CS alone (C) and those exposed to TS plus CS (D) showed increased intra-alveolar macrophages (single asterisk) as well as occasional polymorphonuclear leukocytes inside the alveolar lumina (double asterisks). Areas of focal interstitial alveolitis (long thicker arrows) were seen in both the CS- and CS plus TS-exposed groups (C and D). These lesions consisted of thickened alveolar walls (indicated by short thinner arrows) with increased number of macrophages, pneumocytes, and round mononuclear cells. The bar in all panels equals 50 µm and the magnification ×400.