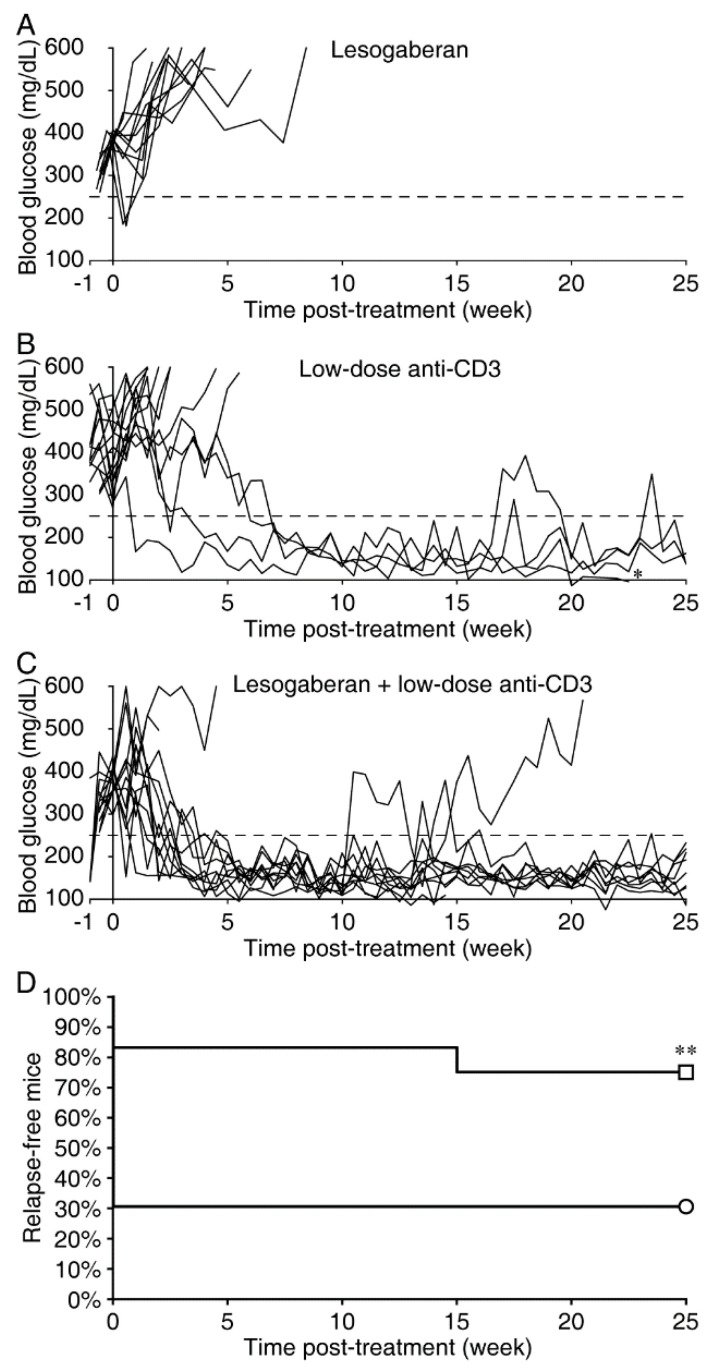
Figure 2.
Combined low-dose lesogaberan and anti-CD3 treatment increases the long-term disease remission rates in severely diabetic NOD mice. Longitudinal blood glucose readings of individual severely diabetic NOD mice (blood glucose of 340–550 mg/dL) that were given lesogaberan (0.08 mg/mL) (n = 11) (A), low-dose anti-CD3 (n = 13) (B), or combined low-dose anti-CD3 and lesogaberan (0.08 mg/mL) (n = 12) (C). * Died of unknown causes. (D) Data show the percents of relapse-fee mice in groups of mice given anti-CD3 (⚪) or the combination of anti-CD3 and lesogaberan (□) for 25-weeks following the treatment. **p = 0.01 as determined by the log-rank test. These studies were run concurrently with studies of combined homotaurine and low-dose anti-CD3 treatment, and the control anti-CD3 group data were previously presented in [16].