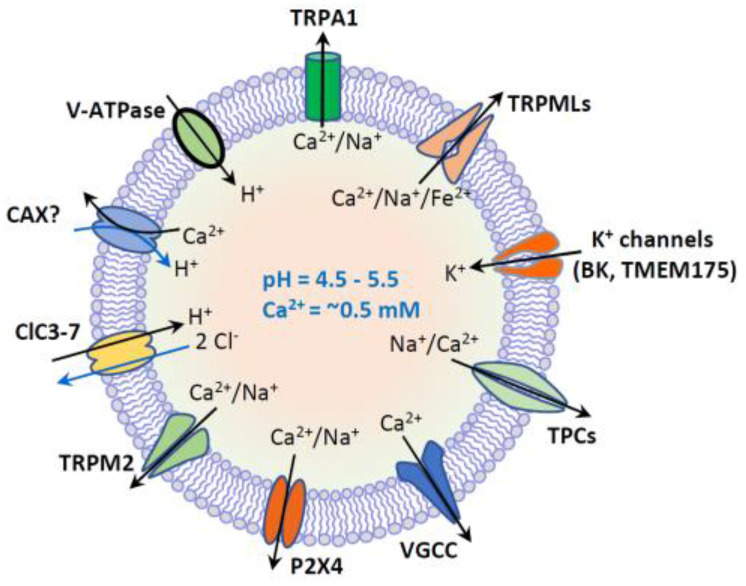
Figure 2.
Lysosome ion homeostasis and ion channels. The lysosome has an acidic lumen that contains soluble hydrolytic enzymes. The activity of hydrolytic enzymes is controlled by intraluminal ion homeostasis that is established by multiple ion channels and transporters. These ion channels and transporters include H+-ATPase, nonselective cation channels (TRPML1-3, TRPM2, TRPA1 and P2 × 4), Na+ or Na+/Ca2+-selective two-pore channels (TPC1-3), voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCC), K+-selective channels (BK and TMEM175), and 2Cl−/1H+ exchanger or Cl−channels (ClC3-7). Putative Ca2+/H+ exchanger (CAX) or Ca2+ transport protein mediates lysosomal uptake of Ca2+. Lysosomal Ca2+ (~0.5 mM) is important for membrane trafficking, and lysosomal pH (4.5–5.5) is essential for the activity of hydrolytic enzymes.