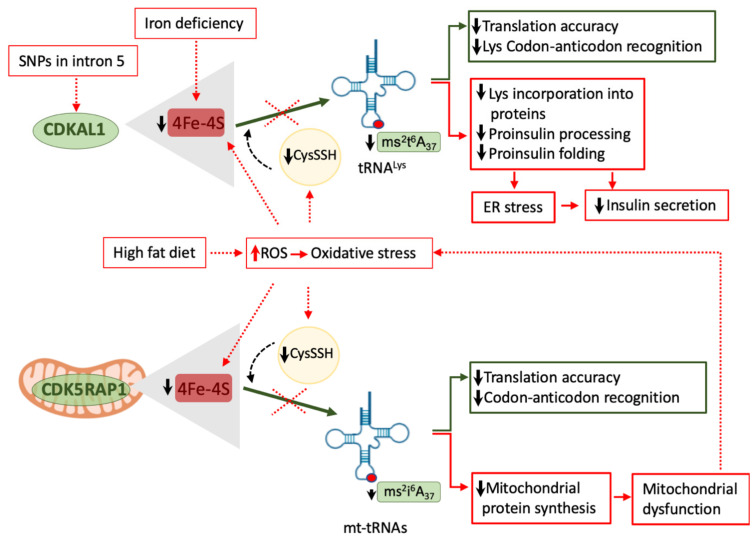
Figure 2.
Genetic and environmental inhibition of tRNA-modifying enzymes. Genetic variants in CDKAL1 have been associated with increased T2D risk. Iron deficiency and oxidative stress (induced by HFD or mitochondrial dysfunction) impair the activity of both CDKAL1 and its mitochondrial homologue CDK5RAP1 by reducing the availability of 4Fe-4S clusters and CysSSH (both needed for their catalytic activity). Impaired CDKAL1 activity results in reduced ms2 modification in cytosolic tRNALys. This causes impaired tRNALys incorporation into proteins (mainly proinsulin), reduced proinsulin processing, proinsulin accumulation in the ER that causes ER stress, and decreased insulin secretion. At the mitochondrial level, impaired CDK5RAP1 function leads to reduced ms2 modification in mt-tRNAs resulting in impaired mitochondrial protein synthesis. This results in mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress that may amplify CDK5RAP1 failure.