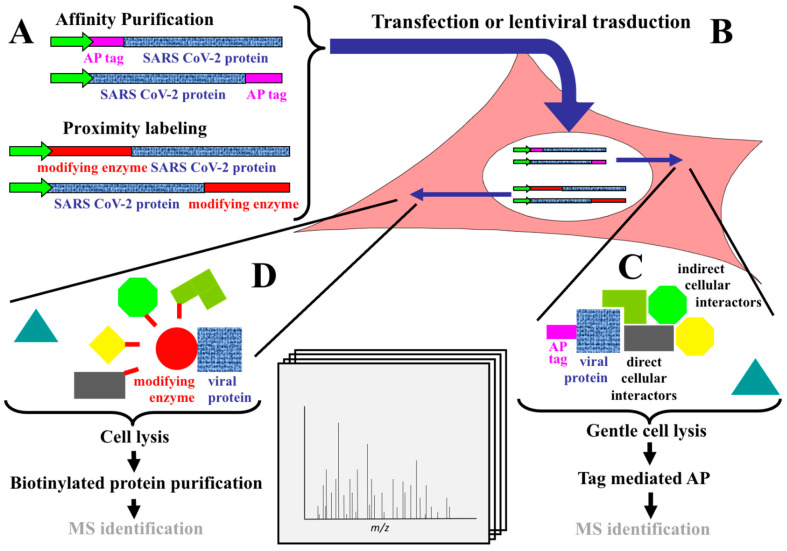
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of (protein–protein interaction) PPI identification strategies. (A) In the Affinity Purification (AP) strategy, the sequence coding for the viral protein (shown in blu) is fused in frame, either at the N- or at the C-terminus, with a peptide tag (shown in purple) which, for the investigations here reviewed, can be Strep [17,18], FLAG [19,20] or HA [21]. In the proximity labeling strategy, the sequence coding for the viral protein is fused in frame, either at the N- or at the C-terminus, with a biotin protein ligase modifying enzyme (shown in red). In all cases, a promoter (green arrow) drives the expression of the fusion protein. (B) The constructs described in (A) are transferred to the test cell line which, for the investigations here reviewed, can be HEK-293 cells [17,18,19,20,23,24] or A549 cells [21,22] by mean of transfection (either transient [17,18,19,20] or stable [23,24]) or by lentiviral mediated transduction [21,22]. In the test cell line, the promoter of the construct drives the expression of the fusion protein. (C) In the AP strategy, following gentle cell lysis, the cellular preys (here shown in different colors and shapes) interacting, either directly or indirectly, with the viral bait are affinity purified, usually using a monoclonal antibody specific for the AP tag (shown in purple). If a cellular protein (indicated by a triangle) does not interact with the viral bait, it is not affinity purified at this stage. Finally, after AP, specifically bound proteins are digested and identified by mass spectrometry (MS). (D) In the proximity labeling approach, after expression of the fusion protein (here shown as a blue square, representing the viral protein, fused with a red circle, representing the modifying enzyme) in the test cell, the biotin protein ligase modifying enzyme mediates the “promiscuous” biotinylation (shown in red) of proteins (here shown in different colors and shapes) in close proximity (~5–10 nm) to the enzyme. If a cellular protein (indicated by a triangle) is not in proximity with the enzyme-viral bait fusion protein, it is not biotinylated. Following cell lysis, only biotinylated proteins are purified by streptavidin and then identified by MS.