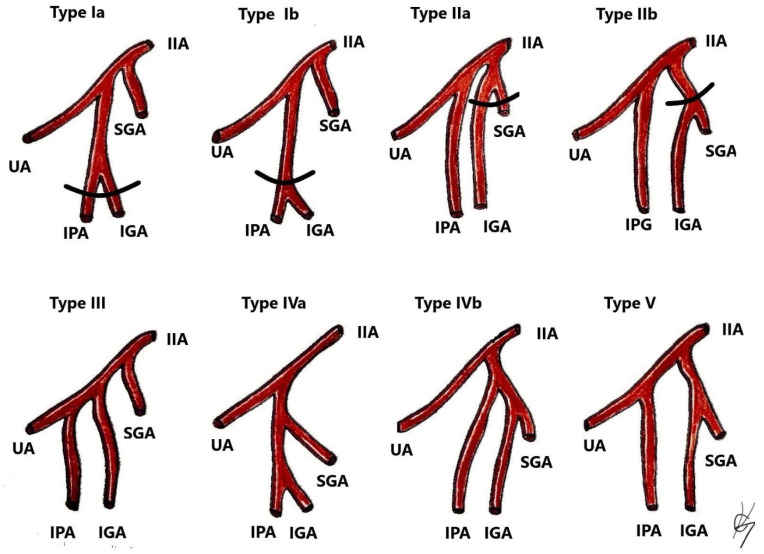
Figure 10.
Classification of IIA variations. Adopted from Adachi [58]. Type I—The superior gluteal artery (SGA) arises separately from internal iliac artery, while the inferior gluteal (IGA) and internal pudendal vessel (IPA) share a common trunk. Type Ia—the bifurcation of IGA and IPA occurs within the pelvis. Type Ib—the bifurcation occurs below the pelvis. Type II—The internal pudendal artery arises separately from the IIA, while the superior gluteal artery shares a trunk with the inferior gluteal artery. Type IIa—the bifurcation of SGA and IGA occurs within the pelvis. Type IIb—the bifurcation occurs below the pelvis. Type III—SGA, IGA, and IPA arise separately from the internal iliac artery, and the internal pudendal artery is the last branch. Type IV—SGA, IGA, and IPA share a common trunk. Type IVA—the SGA is the first vessel from the common trunk, before bifurcating into the other two branches—SGA and IGA. Type IVB—the IPA is the first from the common trunk, which then divides into SGA and IGA. Type V—The IGA has a separate origin from the IIA, while the SGA and IGA share a common trunk.