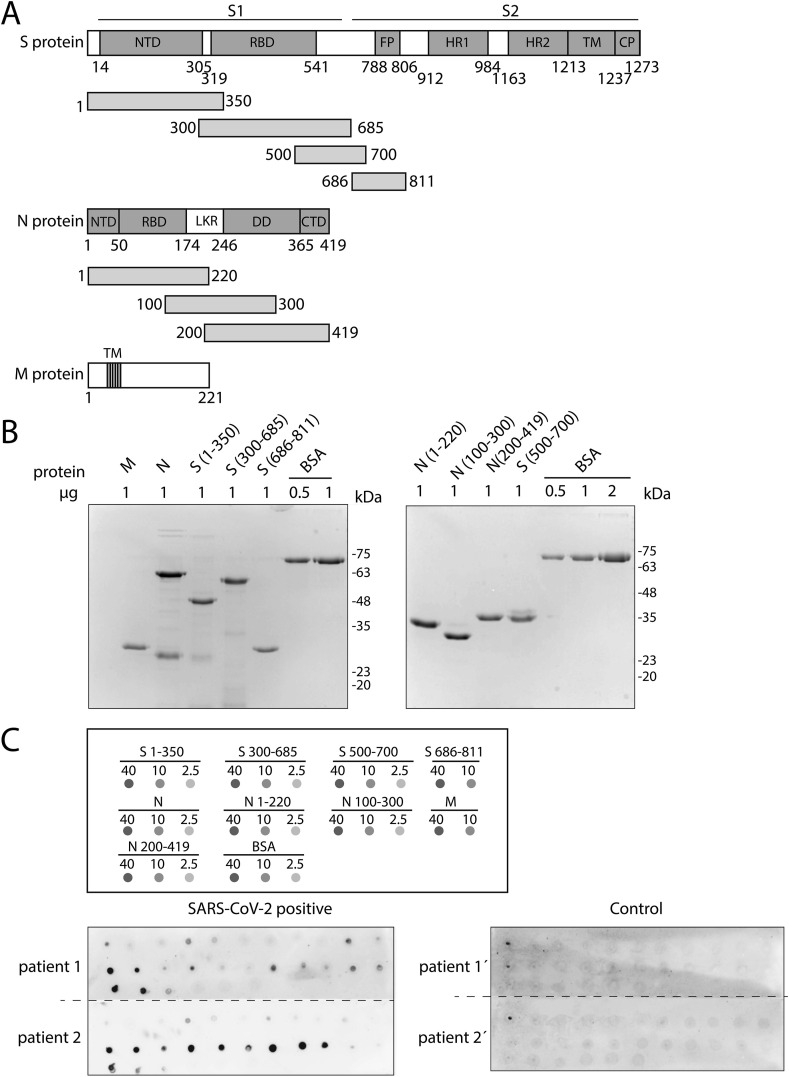
Fig. 1.
Detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 by dot plot. (A) Schematic representation of the different domains in S, N and M proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and the fragments used in this work. For the S protein, the following domains/motifs are indicated: N-terminal domain (NTD), receptor binding domain (RBD), fusion peptide (FP), heptad repeat 1 (HR1), heptad repeat 2 (HR2), transmembrane domain (TM) and cytoplasmic domain (CP). The protein is proteolytically cleaved into two subunits: S1 (amino acids 14–685) and S2 (amino acids 686–1472). N protein-indicated domains are the N-terminal domain (NTD), RNA binding domain (RBD), dimerization domain (DD), a C-terminal domain (CTD) and a linker region (LKR). The 3 transmembrane domains (TM) are shown for the M protein. (B) Coomassie gel staining of all purified proteins used in this study. BSA was used as a control. (C) Top panel displays a diagram of the dot blot design, with the proteins spotted and the amount of protein used (in ng). Bottom panel represents two representative blots developed with sera from SARS-CoV-2 positive (left) and control (right) patients, respectively.