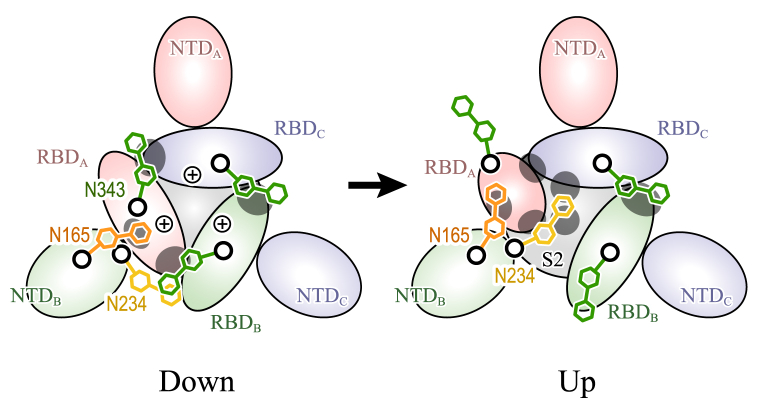
Figure 8.
“Glycan-locking mechanism” for the conformational transition between down and up forms of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein. Major interdomain interactions observed in all-atom MD and TMD simulations are illustrated as gray ellipsoids. Electrostatic interactions between three RBDs give repulsive forces for driving conformational changes from down to up, whereas interdomain contacts and hydrogen bonds between a trimeric structure stabilize the down form with the help of N-glycans at N343. The up form loses interdomain contacts and hydrogen bonds, in particular between RBDB, RBDC, and S2. However, the N-glycan at N234 supports the interaction between them by intruding into the void space. To see this figure in color, go online.