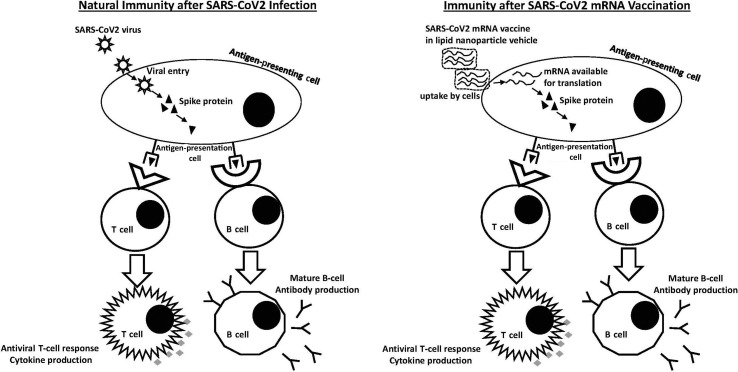
Figure 1.
Natural immunity after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection versus immunity after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. During viral infection, the SARS-CoV-2 virus is taken up by antigen-presenting cells. Individual proteins such as the spike protein are presented to naive T cells and B cells to stimulate specific antiviral T cells and memory B cells to protect against future infection. With mRNA vaccination, mRNA is taken up by cells via the lipid nanoparticle vehicle and is then translated in the cytoplasm to produce spike protein. This spike protein is then presented by antigen-presenting cells in the same way as during viral infection with the same downstream production of antiviral T cells and memory B cells.