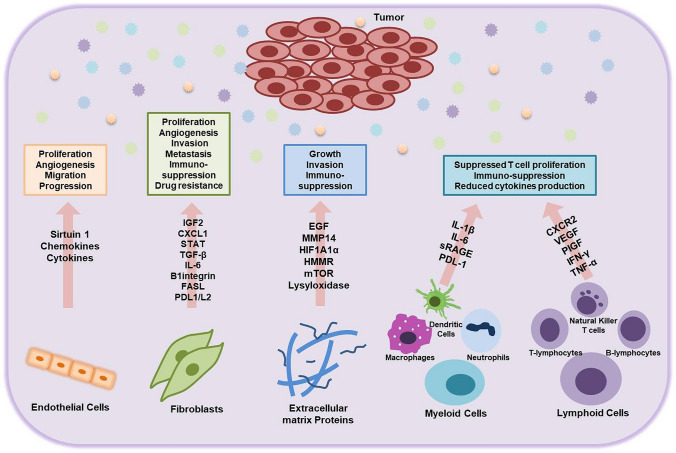
Fig. 1.
Tumor microenvironment (TME) in lung cancer. The TME components support the tumor growth and secrete signals and initiate cascades that facilitate the proliferation, growth, migration, invasion, and stabilization of tumor cells. They also suppress immune responses and confer drug resistance. IGF2 (insulin-like growth factor-2), CXCL1 (C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 1), STAT (Signal Transducer And Activator Of Transcription), TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor Beta), IL-6 (Interleukin-6), FASL (Fas Ligand), PDL1/L2 (Programmed cell death protein ligand 1 and 2), EGF (Epidermal growth factor), MMP14 (Matrix metalloproteinase 14), HIF1A1α (Hypoxia-inducible factor 1A1alpha), HMMR (Hyaluronan mediated motility receptor), mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin), IL-1β (Interleukin-1beta), sRAGE (soluble Advanced Glycosylation End-Product Specific Receptor), CXCR2 (C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 2), VEGF (Vascular endothelial growth factor), PIGF (Placental growth factor), IFN-γ (Interferon-gamma), TNF-α (Tumor necrosis factor-alpha)