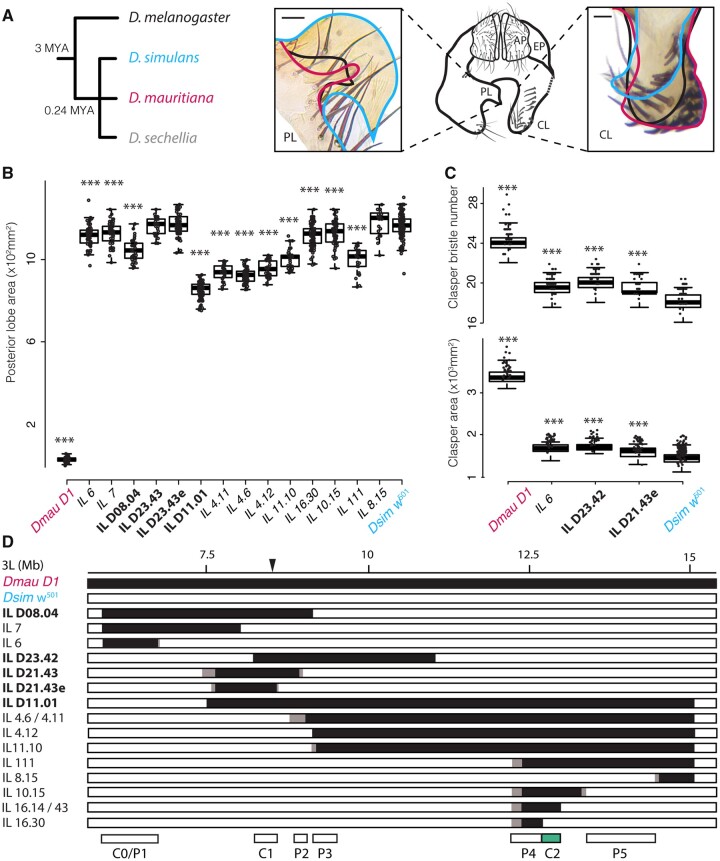
Fig. 1.
Differences in external male-terminal structures among Drosophila melanogaster subgroup species and introgression mapping between D. simulans and D. mauritiana. (A) Relationships of D. melanogaster and species of the D. simulans clade (left). The central diagram depicts a schematic of male genital arch morphology of D. melanogaster (posterior view). The posterior lobes (left-hand box) typically obscure visualization of the claspers (right-hand box), and therefore they are shown here dissected away on the right-hand side of the central schematic. The relative size and shape of the lobes and the claspers of D. melanogaster (black), D. simulans (blue), and D. mauritiana (red) are illustrated in the left and right schematics and images, respectively. D. simulans has much larger posterior lobes and smaller claspers, with fewer, thinner, and shorter bristles than D. mauritiana and D. melanogaster. Posterior lobes (PL), claspers (CL), anal plates (AP), and epandrium (EP). Scale bars = 20 µm. (B–D) Mapping and phenotypic effect of candidate regions on posterior lobe size (B), clasper bristle number (C, upper plot), and clasper area (C, lower plot). Boxes indicate the range, upper and lower quartiles, and median for each sample. Asterisks indicate significant comparisons with Dsim w501 where P < 0.001*** (Dunnett’s test for posterior lobe and clasper size, Dunn’s test for clasper bristle number, supplementary file 2D–F, Supplementary Material online). Differences in the effect of the introgressed regions (supplementary file 3 and supportive text, Supplementary Material online) on posterior lobe size (B) and clasper size/bristle number (C), allowed refinement of candidate regions P1–P5, C0, and C1 (D). The previously identified C2 region is shown in green (Hagen et al. 2019) (D). Black bars indicate Dmau D1 DNA, white bars indicate Dsim w501 DNA, and gray boxes regions containing break points that have not been precisely determined. The black triangle indicates the position of P-element insertion originally used for generating the introgressions. New introgression lines are shown in nonbold font.