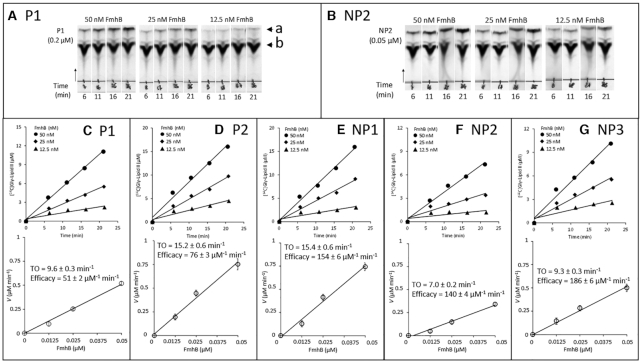
Figure 2.
Impact of the tRNA sequence on the catalytic activity of FmhB in the coupled assay using the hepta-prenyl-containing lipid II analogue as substrate. (A and B) Representative autoradiographies of thin-layer chromatograms for kinetic analyses of FmhB with isoacceptors P1 and NP2, respectively. The arrow heads labeled with the letters a and b indicate the position of the radio-labeled product of the reaction ([14C]Gly-lipid II analogue) and of the [14C]Gly substrate, respectively. The arrow indicates the direction of migration. (C–G) Determination of FmhB activity with various tRNAs. For each isoacceptor, the top panel shows kinetics with three concentrations of FmhB using a fixed concentration of isoacceptor (0.2 μM for P1 and P2; 0.1 μM for NP1; 0.05 μM for NP2 and NP3). Preliminary investigations (data not shown) showed that these concentrations were rate limiting. The values of the velocity (V) of the formation of the radio-labeled product of the reactions ([14C]Gly-lipid II analogue) ± standard deviation were obtained by fitting a first order equation to the data obtained for each enzyme concentration. For each isoacceptor, the bottom panel shows the determination of the turnover (TO; V/FmhB concentration) ± standard deviation, which was obtained by fitting a first order equation to the data. Estimates of the efficacy of FmhB were obtained by dividing TO by the tRNA concentration.