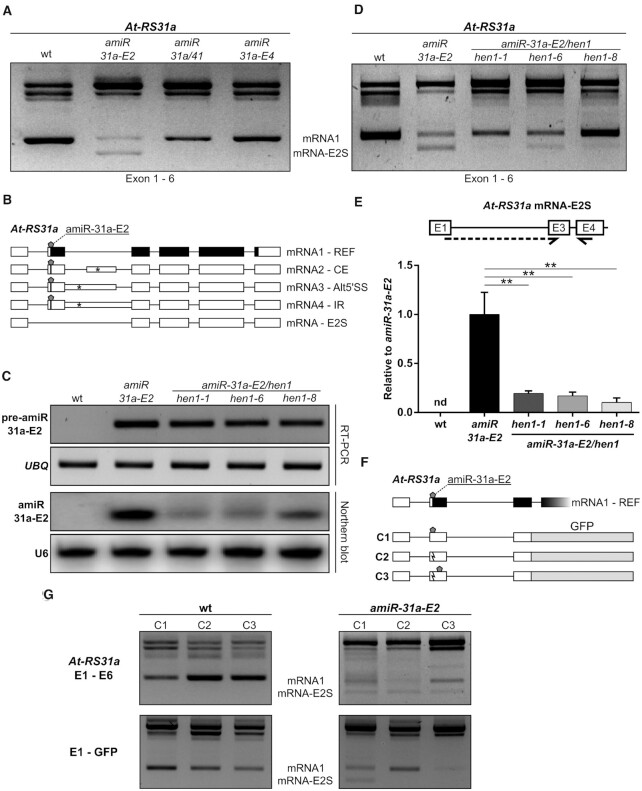
Figure 7.
Artificial miRNA amiR-31a-E2 induces exon 2 skipping in At-RS31a. (A, B) The novel At-RS31a splice variant mRNA-E2S is generated by skipping of the second exon (E2S), which contains the amiR-31a-E2 target site. RT-PCR analysis (A) of At-RS31a performed using primers located in exons 1 and 6 reveals mRNA-E2S in amiR-31a-E2 transgenic plants. (C) Mature amiR-31a-E2 abundance is low in the hen1 mutant background. RT-PCR and Northern blot analyses of precursor pre-amiR-31a-E2 and mature amiRNA amiR-31a-E2, respectively, in amiR-31a-E2/hen1 crosses, amiR-31a-E2 transgenic line and wild type (wt) plants. UBQ1 and U6 snRNA were used as loading controls for RT-PCRs and Northern blots, respectively. (D, E) The accumulation of the At-RS31a mRNA-E2S isoform depends on the mature amiR-31a-E2. (D) RT-PCR analysis of At-RS31a in amiR-31a-E2/hen1 crosses in comparison to amiR-31a-E2 transgenic line and wild type plants, using primers located in exon 1 and exon 6. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of At-RS31a mRNA-E2S levels in amiR-31a-E2/hen1 crosses in comparison to amiR-31a-E2 transgenic line and wild type plants. Partial gene model is shown to visualize analyzed region and primer locations. Primers are shown by arrows. Dashed arrows represent primers spanning exon junctions. Expression was normalized to PP2AA3 and plotted relative to amiR-31a-E2 transgenic plants since mRNA-E2S was not detectable (nd) in wild type. Data represent means ± standard deviation (n ≥ 3). Student's t-test: **P < 0.01. (F, G) The exon skipping event triggered by amiR-31a-E2 depends on the proximity of the amiRNA binding site to the exon border. (F) Minigene constructs corresponding to exons 1–3 of At-RS31a fused to GFP. Construct C1 contains the original amiR-31a-E2 target site (pentagon) close to the border of exon 2. Mutation in the construct C2 (zigzag line) leads to loss of the amiR-31a-E2 target site and mRNAs resistant to the amiRNA. Construct C3 has this same mutation at the original amiRNA binding site but possesses a functional amiR-31a-E2 target site downstream (pentagon). (G) RT-PCR analysis of endogenous At-RS31a using primers located in exons 1 and 6 (E1–E6) and minigene expression (E1–GFP) in plants transformed with the respective minigene construct. Primers are listed in the Supplementary Table S2.