Figure 2.
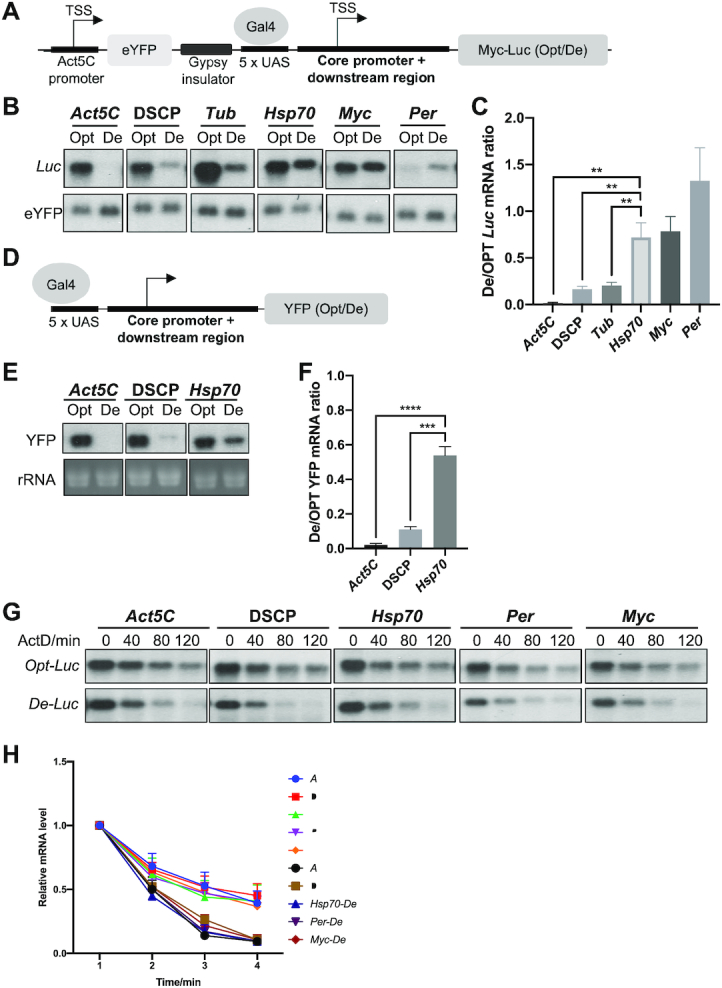
The codon usage effect on gene expression is dependent on promoter. (A) Diagram of the Luc reporter construct. (B) Northern blot analysis of Luc mRNA levels produced from reporter genes driven by indicated promoters. The probe was designed to hybridize to the common 5′ Myc-tag sequence of Luc. (C) Quantification of ratio of De-Luc to Opt-Luc luciferase mRNA ratios normalized by eYFP levels for experiment shown in panel B (n = 3). (D) Diagram of the YFP reporter construct. (E) Northern blot analysis of the YFP mRNA levels produced from reporter genes driven by indicated promoters (upper panel). The probe hybridizes to the common 3′ UTR sequence of YFP genes. rRNA level was used as a loading control. (F) Quantification of the De-YFP/Opt-YFP ratio normalized by rRNA for experiment shown in panel E (n = 3). (G) Northern blot analyses of mRNAs produced from Opt-Luc and De-Luc reporter genes driven by indicated promoters. Actinomycin D was added to the culture at 10 ng/mL at time 0. RNA was isolated at indicated time points, and RNA levels were normalized to eYFP levels. (H) Quantification of Opt-Luc and De-Luc mRNA decay rates for experiment shown in panel G (n = 3). Data are means ± SD. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001. ****P < 0.001. Two-sided Student's t-tests were used.
