Figure 5.
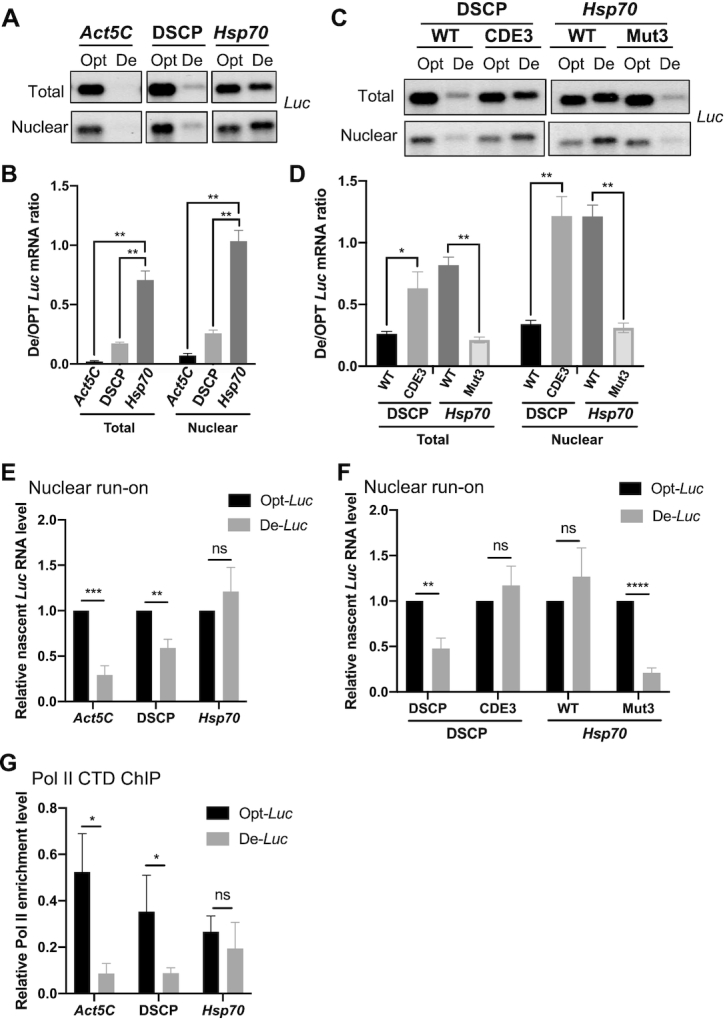
Promoter-dependent codon usage effect is controlled at the level of transcription. (A) Northern blot analysis of De-Luc and Opt-Luc mRNAs expressed under control of indicated promoters in total and nuclear RNA fractions. The probe hybridizes to the 5′ Myc-tag. (B) Quantification of De-Luc and Opt-Luc ratio for experiment shown in panel A (n = 3). (C) Northern blot analysis of De-Luc and Opt-Luc mRNAs expressed under control of DSCP or Hsp70 promoters with wild-type (WT) or mutant CDEs in nuclear and total RNA fraction. (D) Quantification of De-Luc/Opt-Luc ratio for experiment shown in panel C (n = 3). (E) Relative nascent De-Luc and Opt-Luc levels expressed under control of indicated promoters detected by qPCR in nuclear run-on assay. qPCR primers amplify the 5′ Myc-tag sequence, and expression was normalized to Act5C (n = 4). (F) Relative nascent De-Luc and Opt-Luc levels expressed under control of indicated promoters detected by qPCR in nuclear run-on assay (n = 4)). (G) Pol II CTD ChIP assay detecting Pol II levels in the 5′ Myc-tag region of different constructs (n = 3). Data are means ± SD. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001. ****P < 0.001. ns: not significant. Two-sided Student's t-tests were used.
