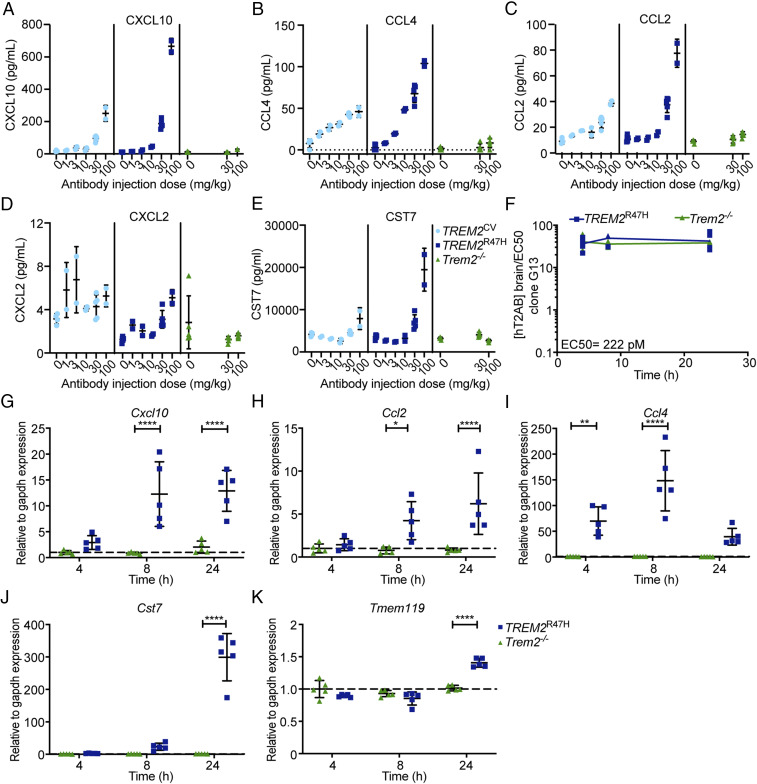
Fig. 2.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of hT2AB. (A–E) Pharmacodynamic study of hT2AB in TREM2CV, TREM2R47H, or Trem2−/− male mice. Different mouse cohorts received a single dose of hT2AB i.v. in the range of 0 (vehicle) to 100 mg/kg for 24 h. Concentrations of chemokines, including CXCL10 (A), CCL4 (B), CCL2 (C), and CXCL2 (D), as well as a microglia activation biomarker CST7 (E), were measured by MSD technology in brain lysates (vehicle, n = 4 for TREM2CV, n = 5 for TREM2R47H or Trem2−/−; 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg, n = 2 for TREM2CV or TREM2R47H; 30 mg/kg, n = 5 for all three genotypes; 100 mg/kg, n = 2 for TREM2CV or TREM2R47H, n = 5 for Trem2−/−). (F–K) A single dose of hT2AB was administered i.v. in TREM2R47H or Trem2−/− male mice at 30 mg/kg. Different mouse cohorts were killed 4, 8, and 24 h after antibody treatment, and brain tissues were collected and lysed for measurement of hT2AB antibody levels and expression of microglial activation biomarkers (n = 5 for each group). (F) hT2AB brain concentration (nanomolar) is ∼25-fold higher than the EC50 values for Syk phosphorylation (222 pM) in clone G13 up to 24 h after i.v. administration of 30 mg/kg hT2AB. qRT-PCR analysis showed increased expression of Cxcl10 (G), Ccl2 (H), Ccl4 (I), and Cst7 (J), as well as the homeostatic microglia marker Tmem119 (K), upon hT2AB treatment. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test; all data are shown as mean ± SD.